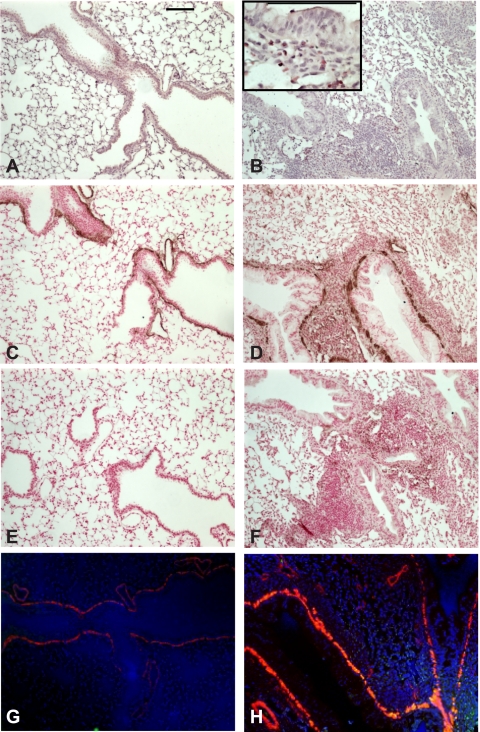
Fig. 3.
OVA treatment increases airway inflammation and ASM α-actin immunostaining. A and B: hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained lung sections from PBS- and OVA-treated mice. Inset shows eosinophilic inflammation. C–F: lung sections were immunostained with anti-α-actin (C and D) or mouse IgG (E and F) and peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse IgG and subsequently developed with diaminobenzidine and NiCl2. Sections were counterstained with nuclear fast red. G and H: immunofluorescence staining of PBS- and OVA-treated mouse lungs using an anti-α-actin Cy3 conjugate (red) and rabbit anti-pGSK with goat anti-rabbit IgG-Alexa 488 secondary (green channel) antibodies. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342 (blue). OVA-treated mice (B, D, F, and H) showed increased airway inflammation and α-actin immunostaining (D). Magnification is ×200, and black bars represent 100 μm.