Fig. 3.
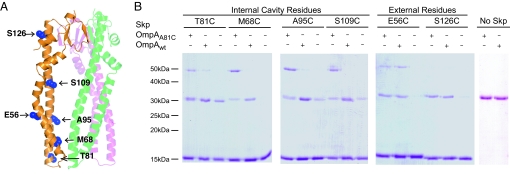
OmpA binding to Skp. (A) Location of single Cys mutations in the Skp monomer are shaded in blue and labeled. Labels on the right point to residues lining the inside of the cavity. Labels on the left point to residues on the outer surface of Skp. The other 2 Skp subunits are shown in faded green and magenta for reference but the Cys residues are not shown for clarity. (B) Nonreducing SDS/PAGE analysis of the cross-linking products of single-cysteine Skp mutants to wild-type OmpA (OmpAwt) containing 2 cysteines in the periplasmic domain or OmpA A81C (OmpAA81C) containing an additional Cys in the β-barrel domain. Plus and minus signs indicate the presence or absence of the 2 forms of OmpA in each reaction. Bands of ≈15 kDa correspond to Skp monomers and bands of ≈50 kDa correspond to a Skp1–OmpA1 cross-link. Note that a disulfide-linked Skp dimer (≈31 kDa) comigrates with free OmpA in these gels (compare lanes without OmpA and lanes labeled No Skp).