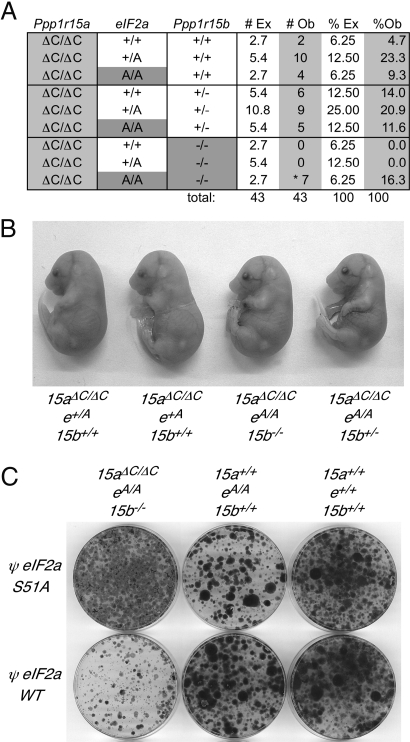
Fig. 6.
Rescue of the early lethality of compound mutant Ppp1r15aΔC/ΔC; Ppp1r15b−/− embryos by the S51A mutation that eliminates the phosphorylation site on eIF2α. (A) Table of genotypes observed in e17.5 embryos isolated from intercrosses of Ppp1r15aΔC/ΔC; eIF2a+/S51A; Ppp1r15b+/− parents with the number and percent of expected (#Ex, %Ex) and observed (#Ob, %Ob) indicated. (*Probability of all 7 Ppp1r15aΔC/ΔC; Ppp1r15b−/− embryos inheriting an eIF2aA/A genotype by chance; P = 6.1 × 10−05.) (B) Photomicrograph of e17.5 embryos isolated from intercrosses of Ppp1r15aΔC/ΔC; eIF2a+/S51A; Ppp1r15b+/− parents (abbreviated 15aΔC/ΔC; e+/A; 15b+/−). Genotypes are indicated below each embryo. (C) Photograph of crystal violet-stained mouse embryonic fibroblasts of the indicated genotype 10 days after transduction with a Puror-marked retrovirus expressing either a wild-type or a S51A mutant allele of human eIF2α and selection with puromycin.