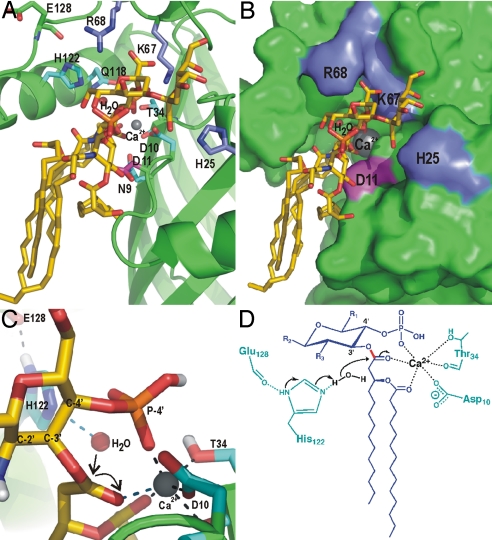
Fig. 4.
Modeling of Kdo2–lipid A into the active site of LpxR and the proposed catalytic mechanism. (A) View of Kdo2–lipid A, which is shown in sticks with yellow carbons, modeled onto LpxR. Fully conserved residues are shown as sticks in cyan. Residues that are probably involved in binding of the Kdo sugars, i.e., K67, R68, and H25 are shown as blue sticks. D11 is shown in magenta. The calcium ion is shown as a gray sphere. (B) LpxR is shown as a surface representation in green with K67, R68, H25, D11, Kdo2–lipid A, and the calcium colored as in A. (C) Closeup of the catalytic site of the modeling result. The representation is the same as in A, with the exception that the view angle is different and that polar hydrogens are shown in white. (D) Proposed catalytic mechanism for LpxR. The substrate is shown in blue, protein residues are shown in cyan, the water and calcium are shown in black. The scissile bond is shown in red. Black arrows indicate the movement of the electron pairs.