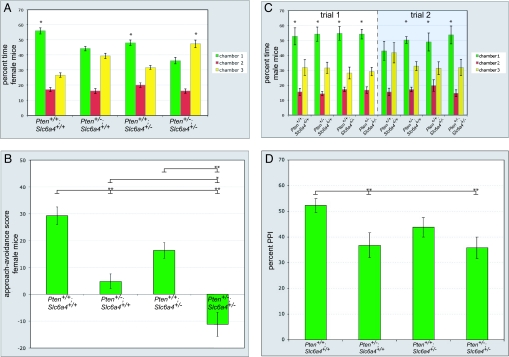
Fig. 3.
Social behavior and prepulse inhibition in Pten and Slc6a4 haploinsufficient mice. (A) Social approach data for 8-week-old female Pten+/+; Slc6a4+/+ (n = 13), Pten+/−; Slc6a4+/+ (n = 13), Pten+/+; Slc6a4+/− (n = 11), and Pten+/−; Slc6a4+/− (n = 13) mice. *, P < 0.05, ANOVA within-group comparison between chamber 1 and chamber 3. Error bars indicate SEM. (B) Social approach data from A presented as approach–avoidance score for analysis across genotypes. Time spent with a social stimulus mouse in chamber 1 is significantly decreased in Pten+/−; Slc6a4+/− mice as compared to Pten+/+; Slc6a4+/+, Pten+/−; Slc6a4+/+, and Pten+/+; Slc6a4+/− mice (F3,49 = 25.3; P < 0.001). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 (Tukey's HSD test). (C) Social approach and recognition data for 8-week-old male mice. During trial 1, the stimulus (located in chamber 1) and the subject mouse interacted for 10 min. Mice were then separated for 30 min. Trial 2 then took place, during which the subject and the stimulus mouse interacted for 5 min. Pten+/+; Slc6a4+/+ (n = 12), Pten+/−; Slc6a4+/+ (n = 10), Pten+/+; Slc6a4+/− (n = 8), and Pten+/−; Slc6a4+/− (n = 8) mice are shown. *, P < 0.05, ANOVA within-group comparison between chamber 1 and chamber 3. Error bars indicate SEM. (D) Prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle response in 8-week-old Pten+/−; Slc6a4+/− mice. Pten+/−; Slc6a4+/+ and Pten+/−; Slc6a4+/− mice have significant deficits in startle inhibition at a prepulse 16 db above background (F3,46 = 3.6; P < 0.05). *, P < 0.05 (Tukey's HSD test). n = 11 Pten+/+; Slc6a4+/+ (8 female), 10 Pten+/−; Slc6a4+/+ (7 female), 13 Pten+/+; Slc6a4+/− (7 female), and 13 Pten+/−; Slc6a4+/− (9 female) mice.