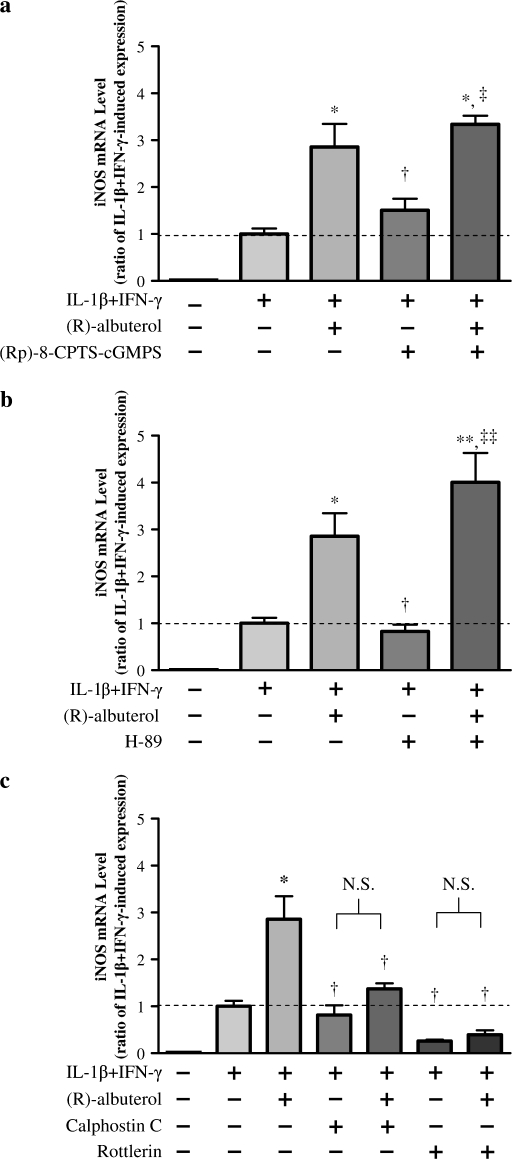
Figure 7.
(R)-albuterol–mediated augmentation of iNOS message involves protein kinase (PK) C, but not PKA or PKG. NHBE cells were exposed to 10 ng/ml each of IL-1β and IFN-γ for 12 h, together with either the PKG inhibitor (Rp)-8-pCPT-cGMPS (1 μM), the PKA inhibitor H-89 (2 μM), the PKC inhibitor calphostin C (500 nM), or the PKCδ inhibitor rottlerin (3 μM), in the presence or absence of 10−5 M (R)-albuterol. iNOS message, normalized to β-actin message, was assayed by TaqMan real-time RT-PCR after total RNA isolation. Inhibition of PKG (a) or PKA (b) did not affect (R)-albuterol–mediated iNOS message augmentation in cytokine-stimulated cells. (c) The PKC inhibitor calphostin C attenuated (R)-albuterol–mediated augmentation of iNOS message, suggesting PKC involvement in the response. Inhibition of PKCδ with rottlerin negated both the (R)-albuterol–mediated increase in iNOS transcription and also IL-1β + IFN-γ–induced iNOS transcription. There was no detectable constitutive iNOS expression in these cells. Dashed line represents IL-1β + IFN-γ–induced iNOS expression. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3–7). * Significantly greater than cytokine-induced iNOS expression (P < 0.01, ** P < 0.001); ‡ significantly greater than inhibitor treated control (P < 0.01, ‡‡ = P < 0.001); † significantly lower than cytokine + (R)-albuterol–treated iNOS expression (P < 0.05). N.S., no significant difference (P > 0.05).