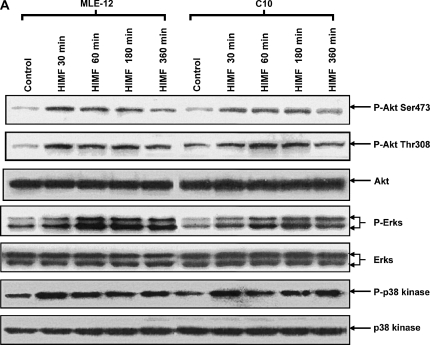
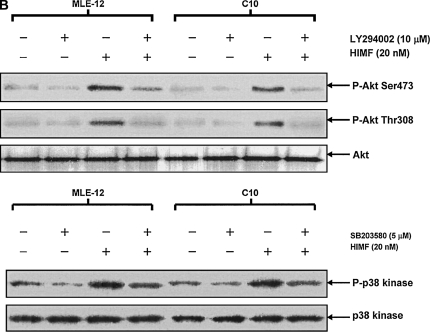
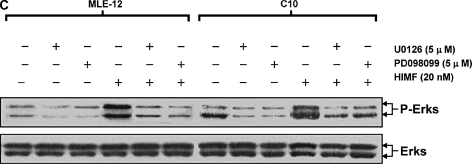
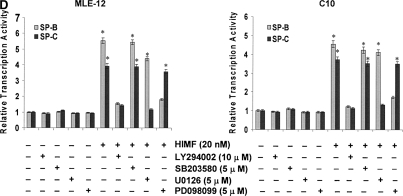
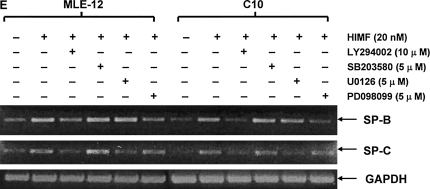
Figure 6.
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI-3K)/Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) were involved in HIMF-induced SP-B and SP-C production. Confluent monolayers of MLE-12 and C10 were starved with medium supplemented with 0.1% FBS and 2 mM L-glutamine. After 33 h, cells were incubated in serum-free medium for 3–4 h at 37°C. Cells were then pretreated with different signal transduction inhibitors for 1 h, and then stimulated with HIMF protein for various periods, as indicated. (A) Western blot with proteins from cell lysate indicated that HIMF strongly activated Akt phosphorylation at Ser473 and Thr308, and phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK. (B and C) The PI-3K inhibitor LY294002 (10 μmol/liter) inhibited HIMF-activated Akt phosphorylation. Moreover, incubation of cells with SB203580, inhibitor against p38 (5 μmol/liter), and either PD098059 (5 μmol/liter) or U0126 (5 μmol/liter), inhibitors of ERK1/2 MAPK pathways, also blocked HIMF-induced phosphorylation of p38 and ERK1/2. (D) Luciferase assay revealed that HIMF-induced SP-B and SP-C expression was not abolished by p38 inhibitor SB203580. However, incubation of MLE-12 cells with the PI-3K inhibitor, LY294002, prevented HIMF-induced upregulation of both SP-B and SP-C. Meanwhile, the inhibitors of ERK1/2 MAPK, PD098059 and U0126, also blocked HIMF-induced SP-B and SP-C production, respectively, which was further confirmed by RT-PCR (E). * Significant increase compared with MLE-12 controls treated without HIMF (P < 0.05). Three experiments with triplicate for each treatment were performed, and all with similar results.