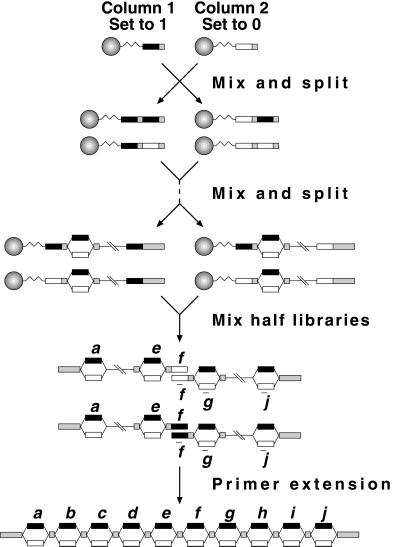
Figure 1.
Modular construction of the combinatorial DNA library from two half-libraries. Linear mixing and splitting steps yield exponential increases in pool complexity. Each half is synthesized on two columns beginning with bit f or its reverse complement. Synthesis of one half continues through bit a and the prefix; the other half contains the reverse complement of bits f through j and the suffix. Because the halves are complementary at position f, primer extension of the two halves creates the full-length 10-bit library. Black and white boxes represent 1 and 0, respectively; shaded boxes represent prefix, suffix, and spacer sequences.