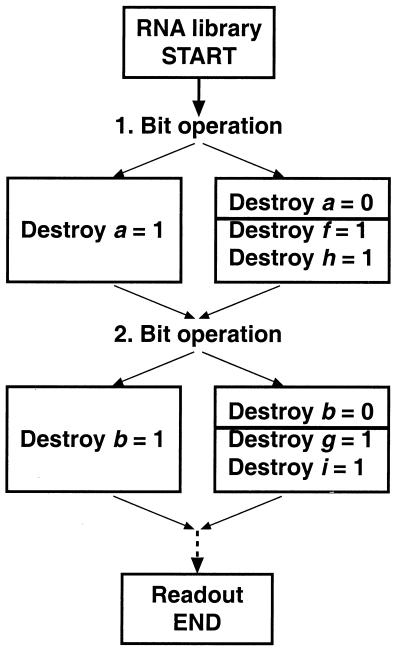
Figure 2.
Outline of the RNA algorithm. A value of 1 or 0 is assigned to a specific bit position by destroying all strands in the RNA library which do not have the value at this position (the step shown sets bits a, f, and h). The library is divided into two equal ensembles. In one test-tube, a specific bit position is set to 1 along with its accompanying constraints; in the other set, this bit is set to 0, using targeted digestion by RNase H. Continuing with this series of operations on the combined ensemble of strands leads to execution of the algorithm, which ends with readout of a randomly chosen subset of the surviving strands.