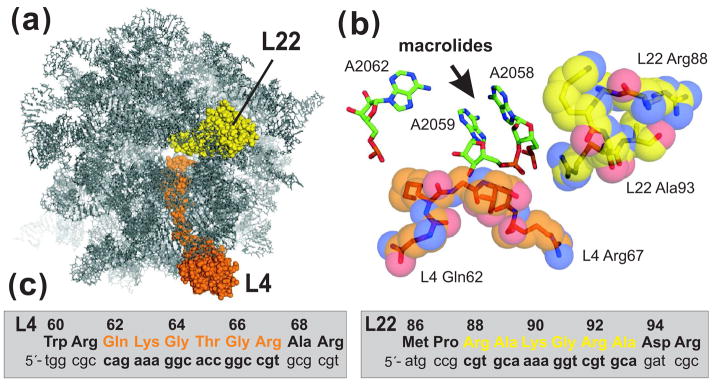
Figure 1.
L4 and L22 loops and the ribosomal macrolide-binding site. (a) The E. coli large ribosome subunit viewed from the cytoplasmic opening of the exit tunnel. All ribosomal proteins except L4 and L22 have been omitted from the rendering. (b) View of the macrolide-binding site. Residues A2058 and A2059 of 23S rRNA form a hydrophobic crevice into which macrolide antibiotics bind. Residue A2062 has been shown to form a reversible covalent bond with the aldehyde moiety of tylosin and spiramycin 1. The tips of the L4 and L22 loops are shown in orange and yellow, respectively. Structures were derived from PDB file 2AW4 45 and rendered using PyMol. (c) L4 and L22 nucleotide and protein sequences. L4 residues Gln62 to Arg67 (in orange) and L22 residues Arg88 to Ala93 (in yellow) were mutagenized by oligonucleotide library recombineering as described in the text.