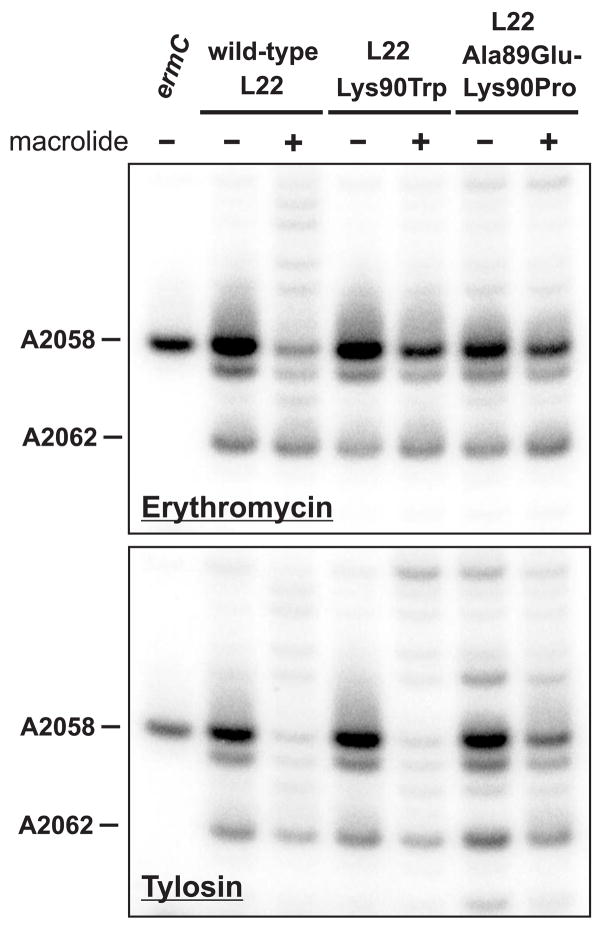
Figure 3.
In vivo methylation protection assays. Wild-type and mutant cells were treated with dimethyl sulfate (DMS) in the presence and absence of macrolide antibiotics (150 μg/mL erythromycin and 1 mg/mL tylosin). Binding of macrolides to the ribosome inhibits DMS-mediated methylation of 23S rRNA residue A2058. Methylation was monitored by primer extension analysis as described in Materials and Methods. Primer extension products corresponding to DMS-mediated N1-methylation of A2058 and A2062 are indicated. Erythromycin had a greater inhibitory effect on DMS-mediated A2058 methylation in wild-type cells compared with the two L22 mutants. Tylosin significantly inhibited DMS-mediated A2058 methylation in wild-type and L22 Lys90Trp cells, but had less of an effect in L22 Ala89Glu-Lys90Pro mutant. A control reaction from cells overproducing the ErmC methyltransferase was included to serve as a marker for A2058 methylation.