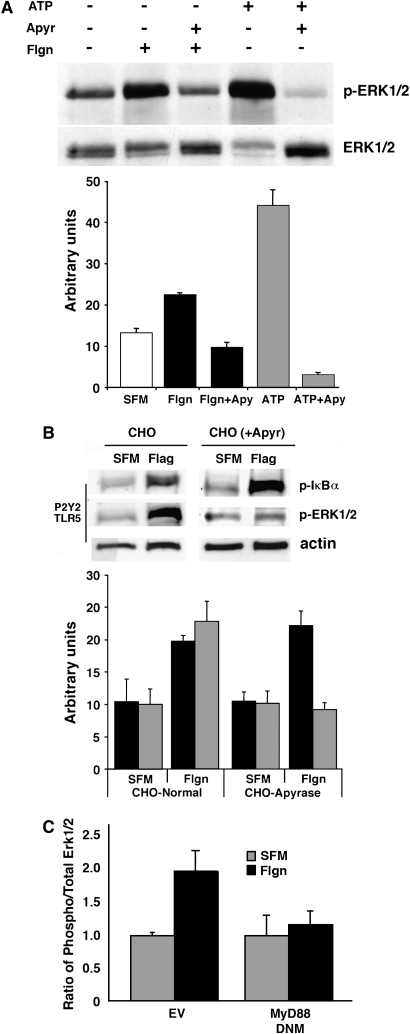
Figure 5.
ATP release in response to flagellin activates Erk1/2. Cell lysates prepared from (A) NCIH292 cells and (B) CHO cells were analyzed by Western blot using antibodies directed against phospho-Erk1/2. Membranes were then stripped and reprobed using an antibody against total Erk1/2 (A) or actin (B). In A, exogenous addition of ATP (100 μM) or flagellin (Flgn, 10μg/ml) for 10 min induced Erk1/2 phosphorylation that was inhibited in the presence of the ATP ectonucleotidase, apyrase (1.5 U/ml). Results from three separate experiments are quantified (mean area ± SEM) by densitometry. (B) Flagellin induced Erk1/2 phosphorylation in CHO cells transiently transfected with TLR5 and the nucleotide receptor, P2Y2. Phosphorylation did not occur in CHO cells overexpressing apyrase (CHO(+Apyr)). In contrast, flagellin-induced IκBα phosphorylation occurred normally in both wild type CHO and CHO(+Apyr) cells. Densitometry was performed to summarize the results (mean area ± SEM) from three separate experiments. IκBα phosphorylation is denoted using solid black bars, while Erk1/2 phosphorylation is denoted by shaded bars. (C) Densitometry data summarizing phospho-Erk/total Erk ratios for flagellin stimulated and DNM MyD88-inhibited NCIH292 cells (mean area ± SEM) shows Erk phosphorylation is Toll like receptor dependent.