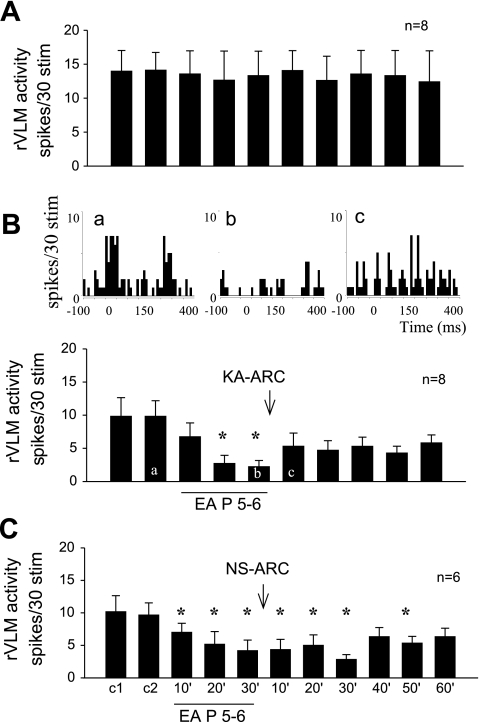
Fig. 1.
Bilateral microinjection of kainic acid (KA) in arcuate (ARC) nucleus blocked electroacupuncture (EA) inhibition of rostral ventrolateral medulla (rVLM) neuronal response to splanchnic nerve stimulation. A: time control of rVLM response to stimulation of splanchnic nerve every 10 min. B, bottom: bilateral microinjection of KA into the ARC nucleus rapidly reversed EA inhibition of the rVLM neural response. *P < 0.05 compared with controls. Top: peristimulus time histograms demonstrate ventrolateral periaqueductal gray (vlPAG) neuronal responses during repeated 15-s (2-Hz) splanchnic nerve stimulations before (a) and after EA (b) at P 5–6 and following KA injection into the ARC (c). C: EA applied bilaterally at P 5–6 acupoints (located over median nerve) for 30 min inhibited splanchnic nerve stimulation-induced rVLM neural responses for more than 50 min. Microinjection of normal saline (NS) into the ARC did not influence the EA-related inhibition.