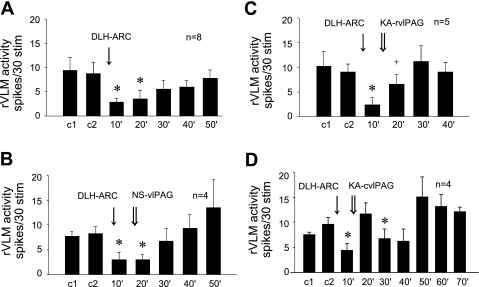
Fig. 3.
Histograms displaying the effect of bilateral microinjection of d,l-homocysteic acid (DLH) and KA in ARC on the rVLM-evoked response to splanchnic nerve stimulation. A: microinjection of DLH in the ARC inhibited rVLM response for 20 min. B: microinjection of NS (vehicle) in the rostral (rvlPAG; n = 2) or caudal (cvlPAG; n = 2) vlPAG did not influence the inhibitory effect resulting from stimulation of the ARC with DLH. C: microinjection of KA in the rvlPAG partially reversed the inhibitory rVLM effect caused by microinjection of DLH in the ARC. D: microinjection of KA in the cvlPAG fully reversed the inhibitory rVLM effect of microinjection of DLH in the ARC *P < 0.05 compared with controls (c1, c2).