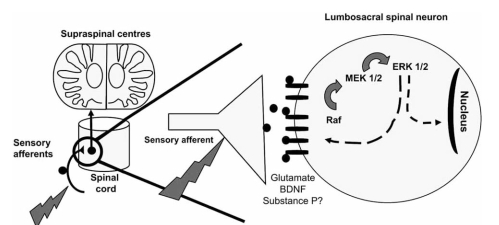
Fig. (3).
Mechanisms of ERK activation in the spinal cord. Upon noxious peripheral stimulation, glutamate and BDNF are released onto the spinal cord. Upon binding to their respective receptors, activation of the pathway occurs in the cytoplasm of spinal neurons. Once activated, ERK can modulate the activity of membrane receptors by phosphorylating specific subunits. Activated ERK can also translocate to the nucleus and induce gene transcription by phosphorylation of transcription factors. The importance of substance P is still in debate.