Abstract
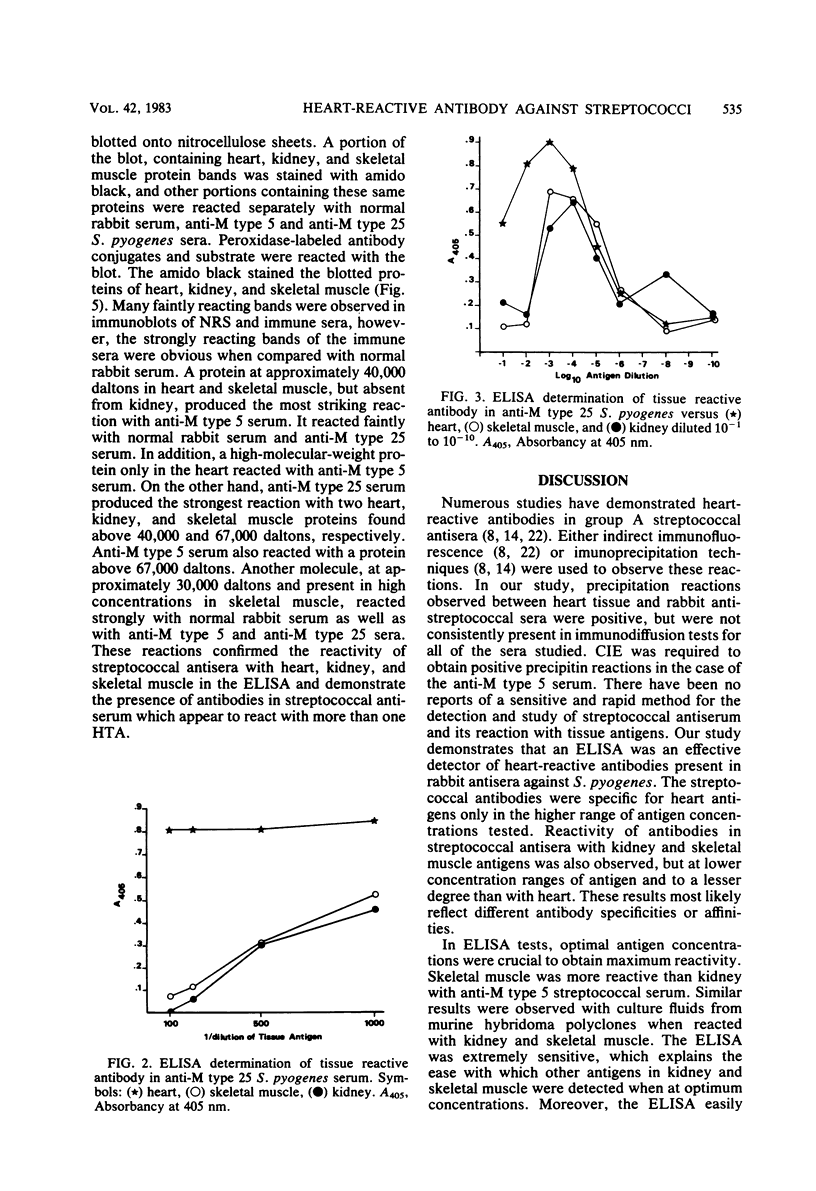
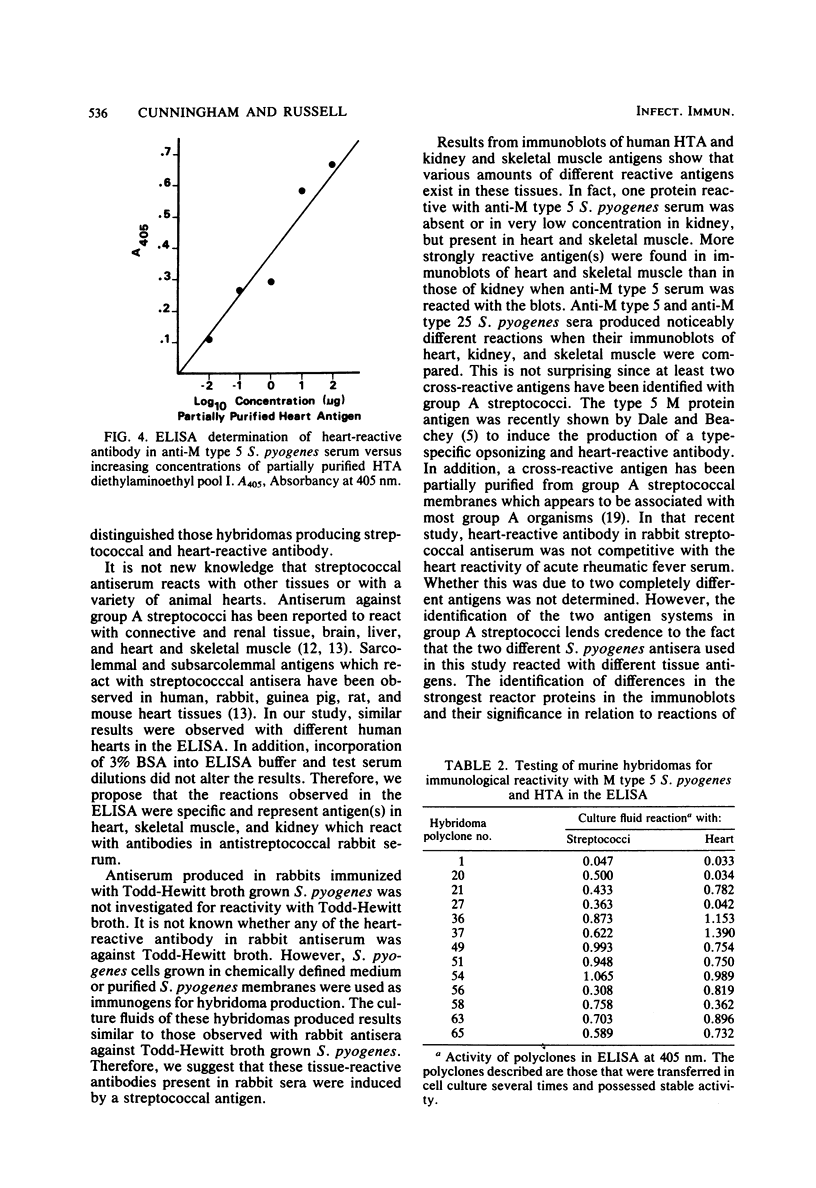
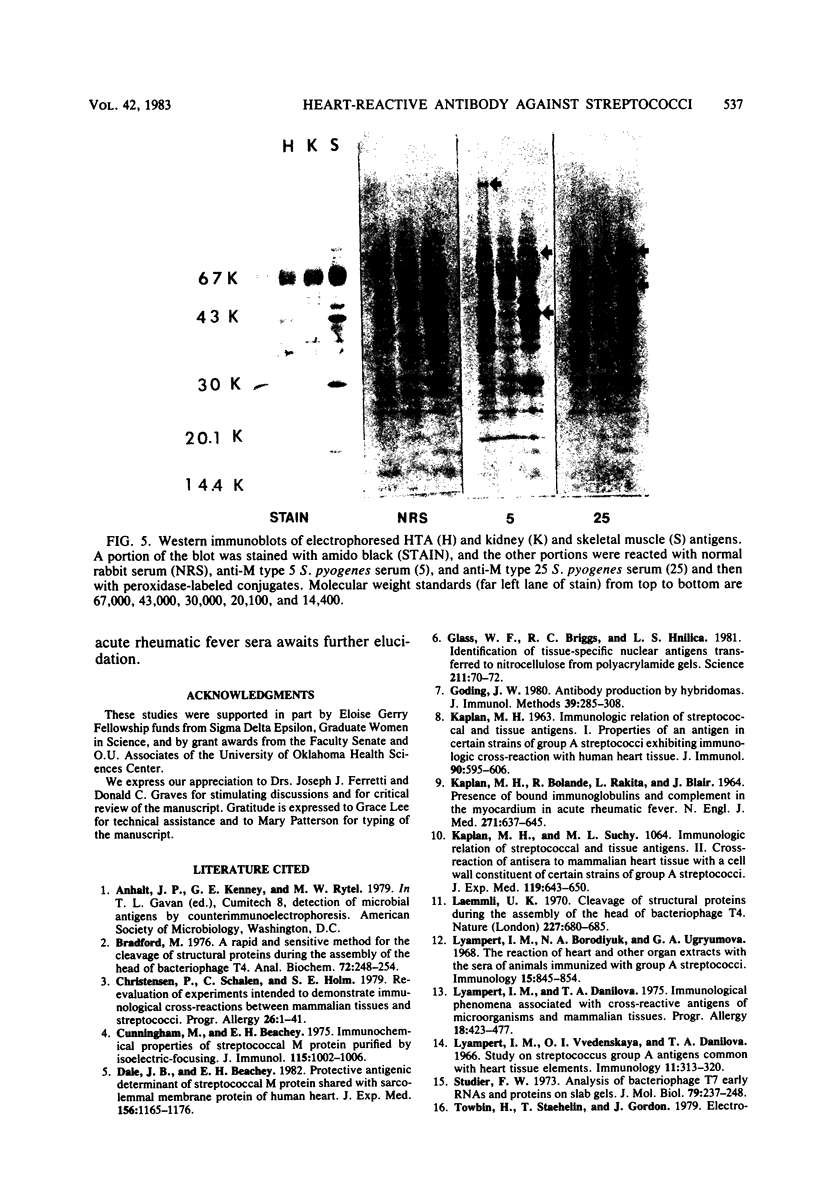
Heart-reactive antibody is known to be produced in animals immunized with group A streptococci. However, the detection and quantitation of these antibodies and their respective antigens have been limited to immunofluorescence or immunoprecipitation tests. In this study a more sensitive technique was used to detect heart-reactive antibody, i.e., the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Countercurrent immunoelectrophoresis and agar gel immunodiffusion were also used to confirm the reactivity of rabbit antisera to group A streptococci and human heart tissue. Human heart tissue antigen was prepared by Triton X-100 extraction, and checkerboard titrations of heart tissue antigen versus streptococcal antisera revealed optimal concentrations of each for the ELISA. When immune rabbit serum was reacted with heart tissue antigen, a 5- to 10-fold increase was observed over the reactions of preimmune sera controls. Streptococcal antiserum was found to have a six- to eightfold greater reactivity with heart tissue antigen than with similar concentrations of kidney and skeletal muscle antigens. Heart tissue antigen was partially purified by DEAE-cellulose chromatography, and quantities of greater than 10 to 100 ng (dry weight) were shown to react with streptococcal antisera in the ELISA. Heart, kidney, and skeletal muscle antigens were subjected to electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel slabs and blotted onto a nitrocellulose filter. These filter blots reacted with streptococcal antisera and confirmed the tissue antigen specificity observed with the ELISA. In addition, the ELISA was found to be an effective method for the detection of heart-reactive antibodies produced by murine hybridomas that were producing antibody to group A streptococci.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen P., Schalén C., Holm S. E. Reevaluation of experiments intended to demonstrate immunological cross-reactions between mammalian tissues and streptococci. Prog Allergy. 1979;26:1–41. doi: 10.1159/000314455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham M., Beachey E. H. Immunochemical properties of streptococcal M protein purified by isoelectric focusing. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):1002–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale J. B., Beachey E. H. Protective antigenic determinant of streptococcal M protein shared with sarcolemmal membrane protein of human heart. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1165–1176. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass W. F., 2nd, Briggs R. C., Hnilica L. S. Identification of tissue-specific nuclear antigens transferred to nitrocellulose from polyacrylamide gels. Science. 1981 Jan 2;211(4477):70–72. doi: 10.1126/science.7003713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Antibody production by hybridomas. J Immunol Methods. 1980;39(4):285–308. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN M. H., BOLANDE R., RAKITA L., BLAIR J. PRESENCE OF BOUND IMMUNOGLOBULINS AND COMPLEMENT IN THE MYOCARDIUM IN ACUTE RHEUMATIC FEVER. ASSOCIATION WITH CARDIAC FAILURE. N Engl J Med. 1964 Sep 24;271:637–645. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196409242711301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN M. H. IMMUNOLOGIC RELATION OF STREPTOCOCCAL AND TISSUE ANTIGENS. I. PROPERTIES OF AN ANTIGEN IN CERTAIN STRAINS OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI EXHIBITING AN IMMUNOLOGIC CROSS-REACTION WITH HUMAN HEART TISSUE. J Immunol. 1963 Apr;90:595–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyampert I. M., Borodiyuk N. A., Ugryumova G. A. The reaction of heart and other organ extracts with the sera of animals immunized with group A streptococci. Immunology. 1968 Dec;15(6):845–854. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyampert I. M., Danilova T. A. Immunological phenomena associated with cross-reactive antigens of micro-organisms and mammalian tissues. Prog Allergy. 1975;18:423–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyampert I. M., Vvedenskaya O. I., Danilova T. A. Study on streptococcus group A antigens common with heart tissue elements. Immunology. 1966 Oct;11(4):313–320. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Rijn I., Bleiweis A. S., Zabriskie J. B. Antigens in Streptococcus mutans cross reactive with human heart muscle. J Dent Res. 1976 Apr;55(Spec No):C59–C64. doi: 10.1177/002203457605500326011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabriskie J. B., Freimer E. H. An immunological relationship between the group. A streptococcus and mammalian muscle. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):661–678. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabriskie J. B., Hsu K. C., Seegal B. C. Heart-reactive antibody associated with rheumatic fever: characterization and diagnostic significance. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Aug;7(2):147–159. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn I., Kessler R. E. Growth characteristics of group A streptococci in a new chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):444–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.444-448.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn I., Zabriskie J. B., McCarty M. Group A streptococcal antigens cross-reactive with myocardium. Purification of heart-reactive antibody and isolation and characterization of the streptococcal antigen. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):579–599. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]