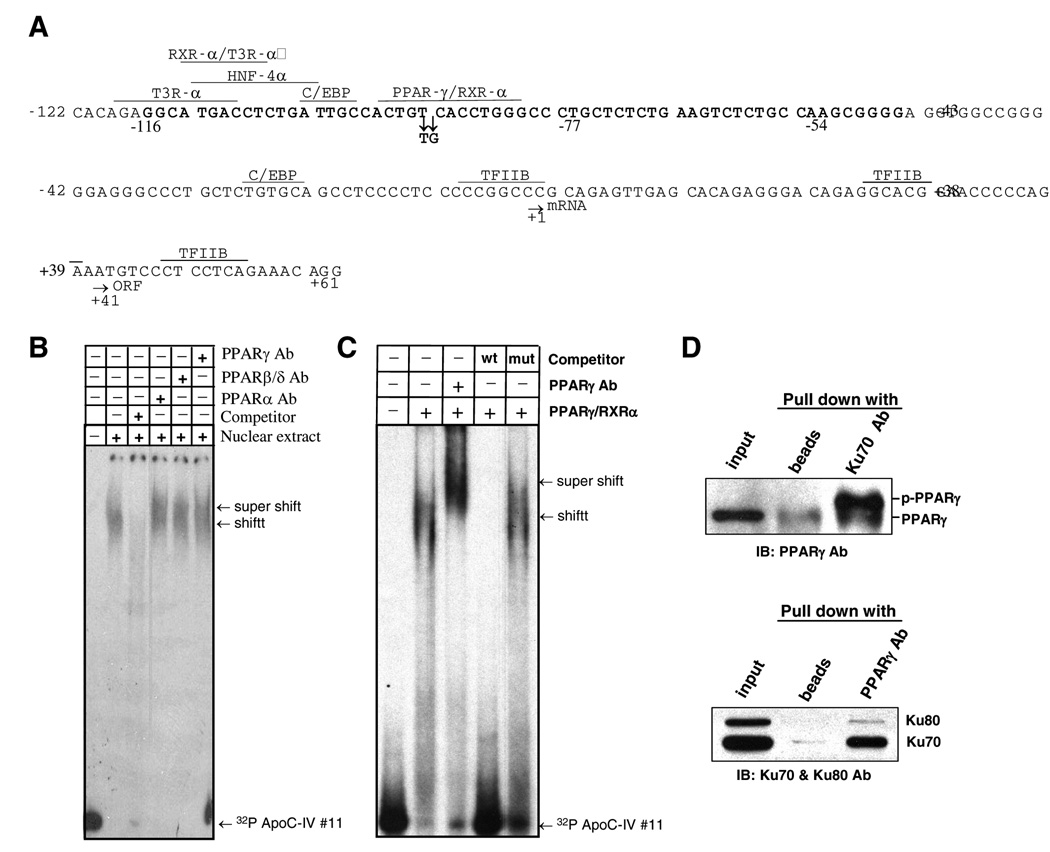
FIG. 5. PPARγ/RXRα association with the 163-bp ApoC-IV promoter and complex formation with Ku70.
(A) Predicted transcription factor binding sites on the 163-bp promoter by TRANSFAC and Genomatix database search. The start sites for transcription (mRNA) and translation (ORF) are indicated by arrows, as well as the two point mutations introduced into the predicted PPARγ/RXRα binding site. Sequence in boldface (−116 to −54) is required for Ku antigen binding. (B) Binding of PPARα, β/δ, and γ to the 163-bp ApoC-IV promoter as indicated by supershift assay using specific antibodies. (C) Gel shift assay to demonstrate binding of purified PPARγ/RXRα to ApoC-IV promoter. Note that PPARγ antibody supershifted DNA band. (C) IP-Western blot analysis to demonstrate association of Ku70 with phosphorylated PPARγ (p-PPARγ). Huh-7 cells were transfected with Ku70 expression plasmid. Cell lysate was immunoprecipitated with Ku70 antibody followed by Western blot detection of PPARγ (upper panel), or immunoprecipitated with PPARγ antibody followed by Western blot analysis of Ku70 and Ku80 (lower panel).