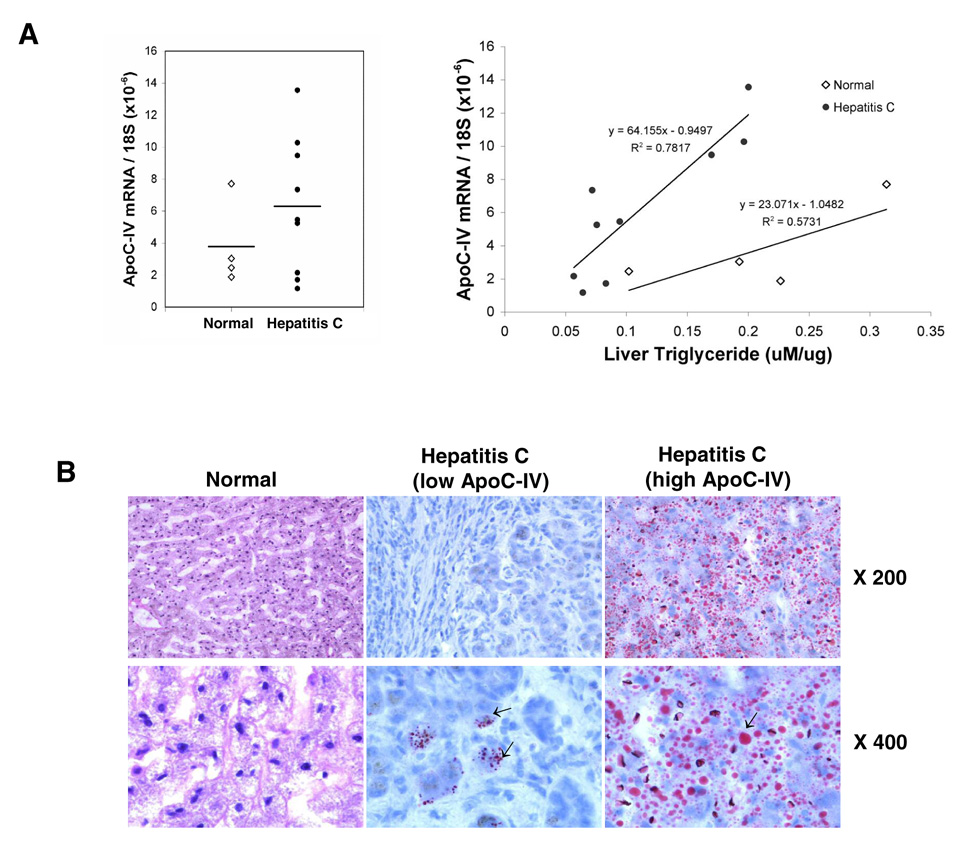
FIG. 8. Correlation of ApoC-IV mRNA level with triglyceride concentration in HCV infected livers.
Nine HCV infected liver tissues were collected at the time of liver transplantation (age: 50.1±4.2; sex: 8 males, 1 female; HCV viral titer: 2.8×103 to 4.9×105 i.u./ml; genotype: 4 1a, 2 1b, 1 3a and 2 ND). Four normal liver tissues were included as controls (age 24.5±13.8; sex: 1 male, 3 females). (A) ApoC-IV mRNA/18S ribosomal RNA (left panel) and its correlation with triglyceride concentration (right panel). The coefficient of determination (R2) and equation are indicated. Open diamond: normal liver. Dark circle: HCV-infected liver. Horizontal bar: average value. (B) Oil-Red O staining of liver sections. The left, middle, and right panels represent normal liver, HCV infected liver with low and high ApoC-IV mRNA level, respectively. Arrows indicate lipid droplets. Note that the genotype difference in triglyceride accumulation was not observed due to limited samples examined.