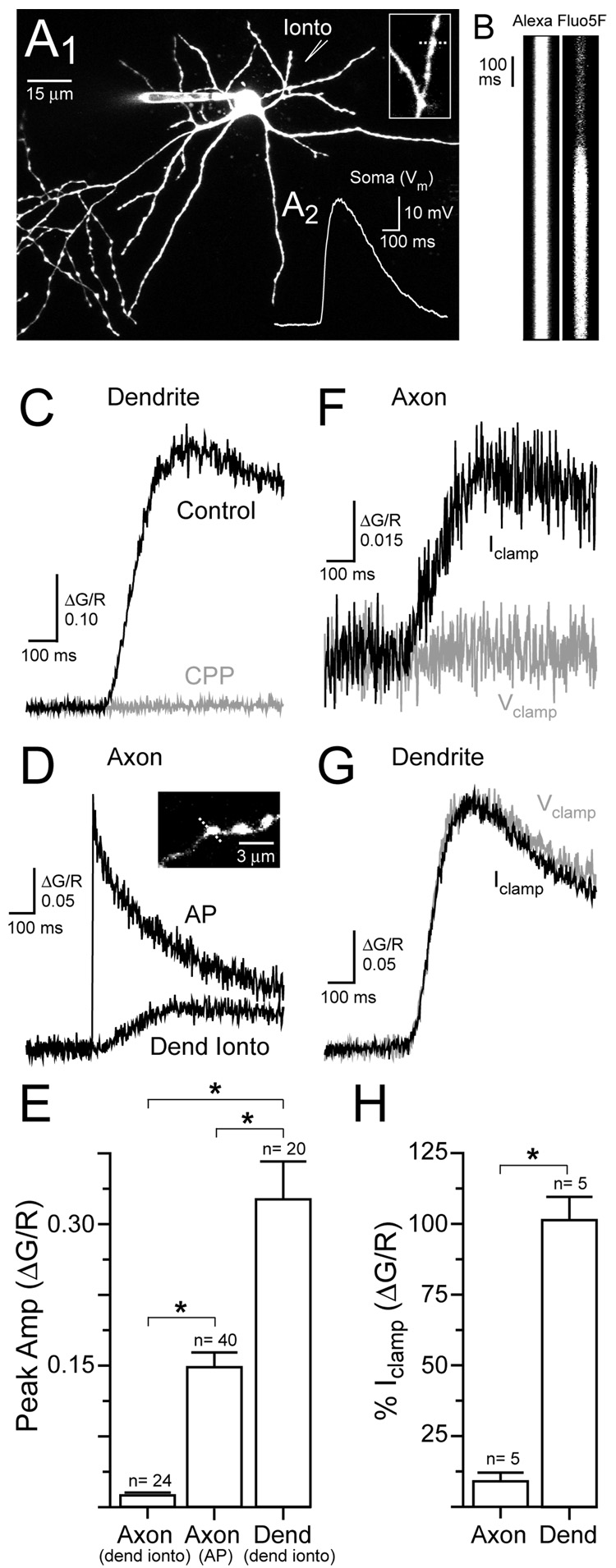
Figure 2. Dendritic NMDAR-mediated Ca2+ entry in axon varicosities.
(A1) Image of a stellate cell shows the location of the iontophoretic pipette used for dendritic L-aspartate application. A magnified view of the dendrite (inset) shows the location of the line scan (dashed line). (A2) Dendritic iontophoresis of L-aspartate evoked an NMDAR-mediated depolarization (Vrest= −71 mV). (B) Line scans from the dendrite in response to L-aspartate iontophoretic stimulation. Iontophoretic pulse lasted 15 msec. (C) The iontophoresis-evoked Ca2+ transient recorded in the dendrite was blocked by the NMDAR antagonist (R)-CPP (20 µM). (D) Ca2+ transients were evoked in an axon varicosity (inset) by an action potential and by dendritic iontophoresis. (E) Average Ca2+ transients evoked in dendrites and axon varicosities. (F) Somatic voltage clamp eliminated the Ca2+ transient evoked in an axon varicosity by dendritic iontophoresis. (G) Somatic voltage clamp did not alter the iontophoresis-evoked Ca2+ transient in a dendrite. (H) Average effect of somatic voltage clamp on Ca2+ transients in axons and dendrites evoked by dendritic iontophoresis.