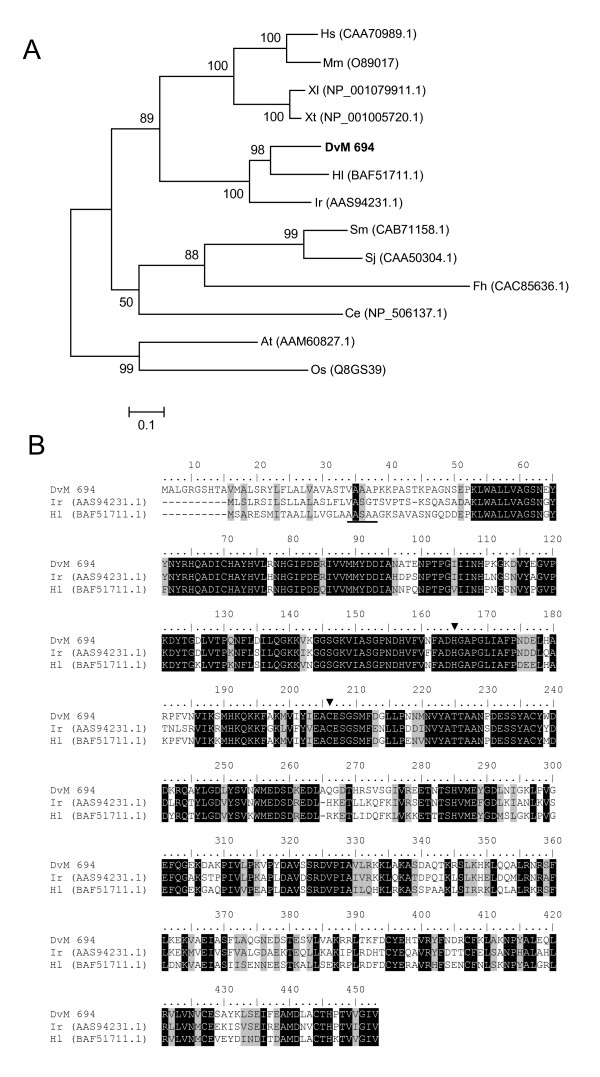
Figure 15.
Analysis of aspartic endopeptidases (AE), a legumain-like family of proteins. (A) Phylogenetic tree based on maximum likelihood analysis of a Dermacentor variabilis midgut protein and published legumain-like sequences. The transcript identified in this analysis is in bold (DvM). Phylogenetic analysis was conducted on protein alignments using Tree Puzzle version 5.2. Values at nodes represent calculated internal branch node support (1000 replications). (B) Multiple sequence alignment (CLUSTALX) of protein sequences identified in a cDNA library of unfed/2 d fed or 6 d fed D. variabilis midguts (DvM) and published sequences from other ticks found on Genbank. Arrowheads indicate conserved His and Cys residues forming the catalytic dyad of AE. Underlined amino acids represent the predicted cleavage position of the signal peptide. Shading represents 100% identity (black) or similarity (grey) among the sequences. Alignments were conducted using CLUSTALX. D. variabilis (Dv), Homo sapiens (Hs), Mus musculus (Mm), Xenopus laevis (Xl), Xenopus tropicalis (Xt), Haemaphysalis longicornis (Hl), Ixodes ricnius (Ir), Schistosoma mansoni (Sm), Schistosoma japonicum (Sj), Fasciola hepatica (Fh), Caenorhabditis elegans (Ce), Arabidopsis thaliana (At), and Oryza sativa (Os).