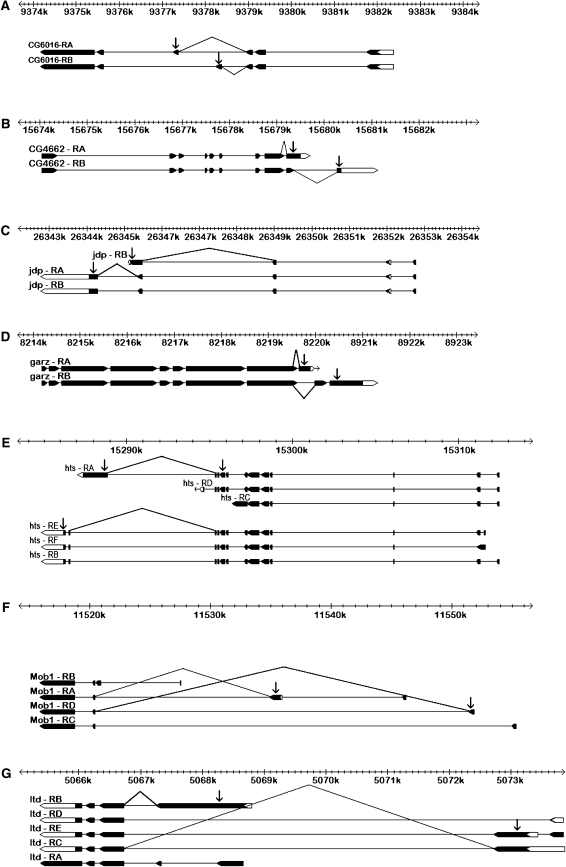
Figure 1.—
Gene structure schematic illustrating transcript targets of exon-specific microarray probes (arrows) and exon-junction RT–PCR primers (connected lines) for each of the seven nonregulatory genes investigated by RT–PCR for D. melanogaster. Exons are shown as boxes (solid boxes, coding regions; open boxes, UTRs) connected by introns (lines), with each transcript aligned against the cytogenic scale. (A) Microarray probes targeting alternatively spliced exons CG6016:7 (transcript CG6016-RA) and CG6016:4 (transcript CG6016-RB) and RT–PCR primers for transcripts CG6016-RA and CG6016-RB. (B) Microarray probes targeting alternatively spliced exons CG4662:9 (transcript CG4662-RA) and CG4662:11 (transcript CG4662-RB) and RT–PCR primers for transcripts CG4662-RA and CG4662-RB. (C) Microarray probes targeting alternatively spliced exons jdp:4 (transcripts jdp-RA and jdp-RB) and jdp:7 (transcript jdp-RC) and RT–PCR primers targeting transcripts jdp-RA and jdp-RC. (D) Microarray probes targeting alternatively spliced exons garz:11 (transcript garz-RA) and garz:9 (transcript garz-RB) and RT–PCR primers targeting transcripts garz-RA and garz-RB. (E) Microarray probes targeting exons hts:16 (transcript hts-RA) and hts:13 (transcripts hts-RB, hts-RE, and hts-RF) and RT–PCR probes targeting transcripts hts-RA and hts-BEF. (F) Microarray probes targeting exons derived from alternative initiation sites, Mob1:6 (transcript Mob1-RA) and Mob1:5 (transcript Mob1-RD) and RT–PCR primers for Mob1-RA and Mob1-RD—note that the microarray results for this gene were not verified by PCR and it was not considered further. (G) Microarray probes targeting exons derived from alternative initiation sites, ltd:7 (transcript ltd:RB), ltd:6 (transcript ltd:RC), and ltd:1 (transcript ltd:RE) and RT–PCR primers for transcript ltd-RB and transcripts ltd-RC and ltd-RE. Gene structures were adapted from FlyBase V. 5.4.