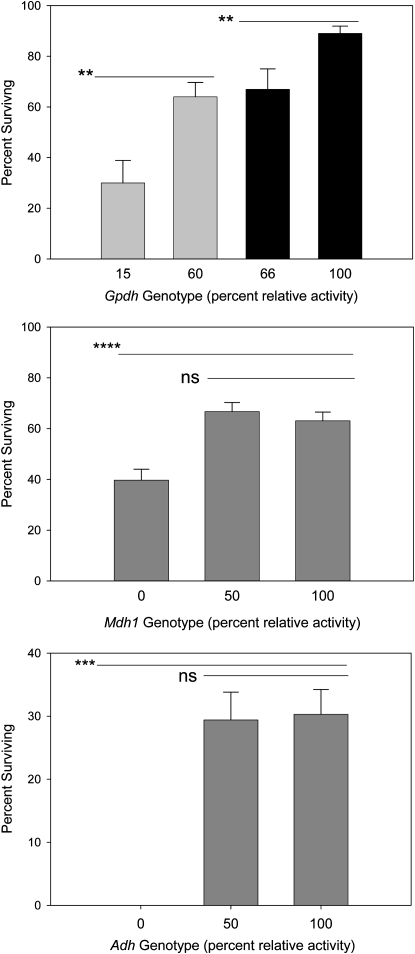
Figure 1.—
Genotype-specific adult (male) survivorship after 48 hr of exposure to a 15% ethanol, 2% sucrose solution. (A) Experiments 1 and 2 using genotypes that possess 10 and 60% normal GPDH activity (shaded bars)—Gpdh9.2/24.1 (n = 17) and Gpdh24.1/10.2 (n = 20)—and (solid) genotypes Gpdh 9.2/6326 (n = 13) and 10.2/6326 (n = 20) possessing 66 and 100% normal activity. (B) Experiment 3 using Mdh1 genotypes 18.1/18.1 (n = 33), 18.1/10.5 (n = 39), and 10.5/10.5 (n = 36), representing 0, 50, and 100% normal MDH activities. The homozygous null genotype has a significantly lower survival rate (P < 0.0001). (C) Experiment 4 using three Adh genotypes: 25/25 (n = 29), 17/25 (n = 33), and 17/17 (n = 35) possessing 0, 50, and 100% normal ADH activity. Error bars represent ±1 SE. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.