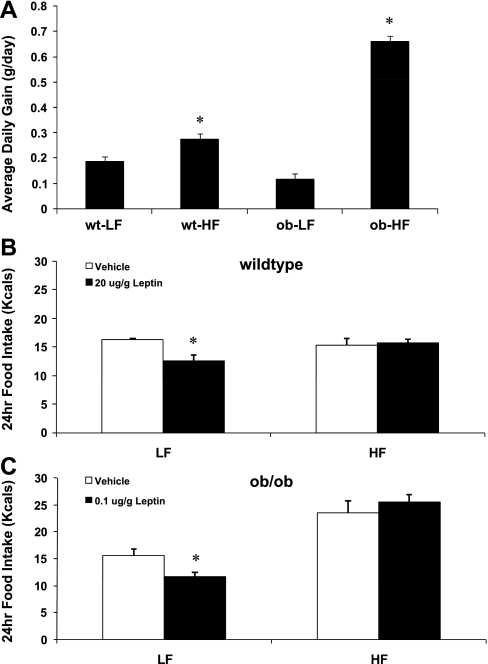
Fig. 6.
Effect of HF diet on body weight gain and leptin sensitivity in control and leptin-deficient mice. Male, leptin-deficient (ob/ob) mice and wild-type controls were fed either a LF or HF diet for 14 days (5 mice/group). On day 14, mice were injected ip with leptin or saline, and 24-h food intake was recorded. A: as noted in the prior study, ob/ob were highly sensitive to the HF diet, increasing body weight gain ∼564% (P = 0.001) when placed on the HF diet compared with an ∼40% increase in body weight gain in wild-type mice on the HF diet (P = 0.004). B: in wild-type mice on a LF diet, leptin (20 μg/g) significantly suppressed 24-h food intake (P = 0.02), but this same dose failed to significantly reduced food intake after 14 days of HF feeding (P = 0.75). C: in ob/ob mice on a LF diet, leptin also suppressed food intake, but at a much lower dose (0.1 μg/g; P = 0.02). However, after 14 days of HF feeding, this dose also failed to significantly suppress food intake (P = 0.40).