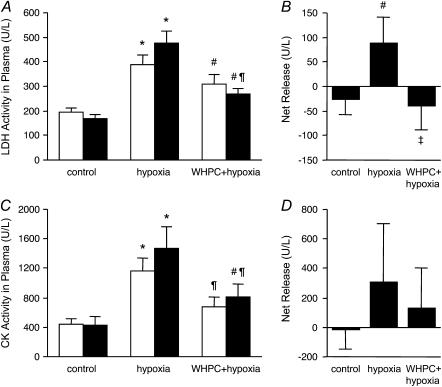
Figure 3.
WHPC reduces hypoxia-induced release of injury markers into the pulmonary circulation. The differences between LDH and CK activities in blood samples collected from the left ventricle (filled bars, pulmonary efferent blood) and those in blood samples collected from the right ventricle (open bars, pulmonary afferent blood) were calculated and taken as the net release of these injury markers from the lung. (A and B) Exposure to hypoxia increased the release of LDH from both peripheral tissues and the lung. Pretreatment with WHPC significantly diminished LDH release from the lung, but had little effect on that from peripheral tissues. *P < 0.001 versus control; #P < 0.05 versus control; ¶P < 0.001 versus hypoxia; ‡P < 0.05 versus hypoxia. (C and D) Exposure to hypoxia increased the release of CK, mainly from peripheral tissues, which was significantly attenuated by pretreatment with WHPC. *P < 0.005 versus control; #P < 0.05 versus control; ¶P < 0.05 versus hypoxia. All data are means ± SE; n = 10 for each group.