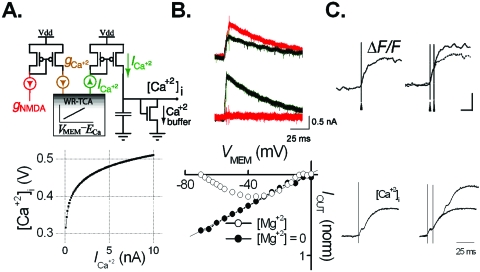
Figure 3. Wide dynamic range aVLSI microchip emulation of NMDA receptor-mediated calcium dynamics.
(A) Top: the NMDA-dependent calcium circuit. The NMDA conductance gNMDA (red) is scaled to generate calcium conductance gCa. This signal is sent to a WR-TCA to generate . is sent to a current-voltage converter circuit to generate [Ca+2]. Bottom: the IIN-VOUT steady-state V-I curve of the current-voltage converter circuit. (B) Top: INMDA (red) and ICa (green) responses to a presynaptic AP at VMEM=−40 and 0 mV, showing the NMDA channel voltage dependence and the presence of while INMDA≈0. Bottom: INMDA-VMEM curve of the NMDA circuit in the presence (○) or absence (●) of [Mg+2] block. (C) Top: biological recording of [Ca+2] integration in response to a single or a pair of presynaptic pulses [adapted by permission from MacMillan Publishers Ltd.: Nature (Mainen 1999), copyright 1999]. Bottom: the circuit response to the same stimulation protocol (time scale apply to both top and bottom.)