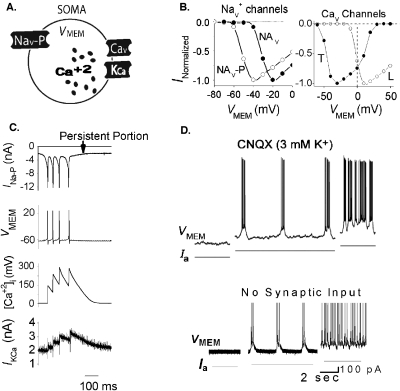
Figure 4. Wide dynamic range aVLSI microchip emulation of pacemaker bursting behavior.
(A) Somatic compartment with Nav–P–persistent Nav channel; Cav–voltage-gated calcium channel; KCa—calcium-dependent potassium channel. VMEM is connected to an integrate-and-fire (I-F) soma circuit for spike generation. (B) Left: IOUT-VMEM curves of Nav channels and of L-type Cav channel and T-type Cav channel (T-spice simulation). (C) Fabricated chip recording of ionic signals during a burst. (D) Top: Biological recording of a pacemaker neuron [reproduced with permission from Del Negro et al. (2005), Copyright 2005 by the Society for Neuroscience]. Bottom: fabricated chip recording from circuit VMEM node. Same scales for both top and bottom.