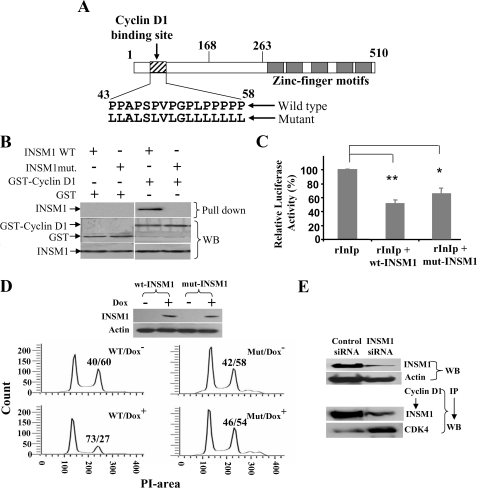
FIGURE 7.
INSM1 proline-rich sequence is required for cyclin D1 binding. A, schematic diagram of the INSM1 mutant. B, GST-cyclin D1 pull-down of wild type and mutant INSM1. GST was used as a control. Either wild type or mutant INSM1 expression vector was transiently transfected into Cos-7 cells. The transfected cell lysate was subjected to a GST-cyclin D1 pull down experiment. C, measurement of transcriptional repressor activity. rInIp driven luciferase vector was transfected alone or with either wild type or mutant INSM1 into β-TC1 cells. Promoter activities were normalized with pCMV-β-galactosidase internal control (**, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05). D, wild type or mutant INSM1 Tet-on Cos-7 cells were subjected to doxycycline induction. As described above, the cells were synchronized with serum-free medium, and subsequently stimulated with 10% serum for 24 h. Western blot analysis showed the expression of both wild type and mutant INSM1 proteins when treated with doxycycline. The cells were subjected to propidium iodide staining and flow cytometric analysis. A G1/S:G2/M ratio is shown above the G2/M peak. E, siRNA knock down of INSM1 in the Cos-7 Tet-on system. INSM1 siRNA treatment suppressed INSM1 expression and restored cyclin D1 and CDK4 interaction. WB, Western blot; wt or WT, wild type; mut, mutant.