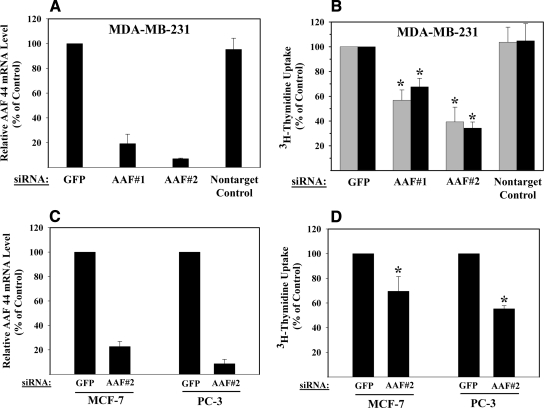
FIGURE 8.
Effect of AAF-44 siRNAs on DNA replication. A, MDA-MB-231 cells were transfected with siRNAs targeting two different sequences in AAF-44 or with control siRNAs (one control siRNA targeting GFP and the other not targeting any known mRNA). Forty-eight hours later, AAF-44 mRNA levels were quantified by real time reverse transcription-PCR. Expression levels were normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mRNA levels, and the relative AAF-44 mRNA level in cells transfected with GFP siRNA was assigned a value of 100%. B, MDA-MB-231 cells were transfected as described in A and grown in medium containing either 0.1% (gray bars) or 10% (black bars) dialyzed FBS. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were incubated with [methyl-3H]thymidine for 4 h, and thymidine uptake into DNA was measured as described under “Experimental Procedures”; the uptake observed in GFP siRNA-transfected cells was assigned a value of 100%. For GFP siRNA-transfected cells grown in 0.1 or 10% FBS, [methyl-3H]thymidine uptake into DNA was 42,040 ± 14,545 and 149,175 ± 48,030 cpm/105 cells/h, respectively. C, MCF-7 and PC-3 cells were transfected with siRNAs targeting GFP or AAF-44, and AAF-44 mRNA levels were quantified as described in A. D, MCF-7 and PC-3 cells were transfected as in C and transferred to medium containing 0.1% FBS, and [methyl-3H]thymidine uptake into DNA was determined as in B. Asterisk, p < 0.05 for the comparison between cells transfected with AAF siRNA versus GFP siRNA. Shown are the means ± S.D. of at least three independent experiments.