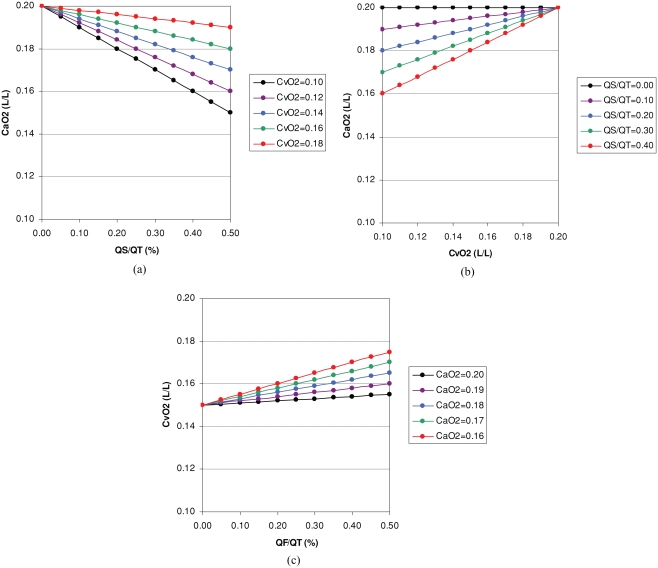
Figure 1.
Theoretical calculations based on the classical shunt equation: (a) Effect of venous admixture or pulmonary shunt fraction () on arterial oxygen content (CaO2) for a given mixed venous oxygen content () assuming ideal pulmonary capillary oxygen content is 0.20 L/L; (b) effect of on CaO2 for a given also assuming ideal pulmonary capillary oxygen content is 0.20 L/L; and (c) effect of an arteriovenous stula expressed as a fraction of cardiac output () on for a given CaO2 assuming systemic capillary oxygen content is 0.15 L/L.