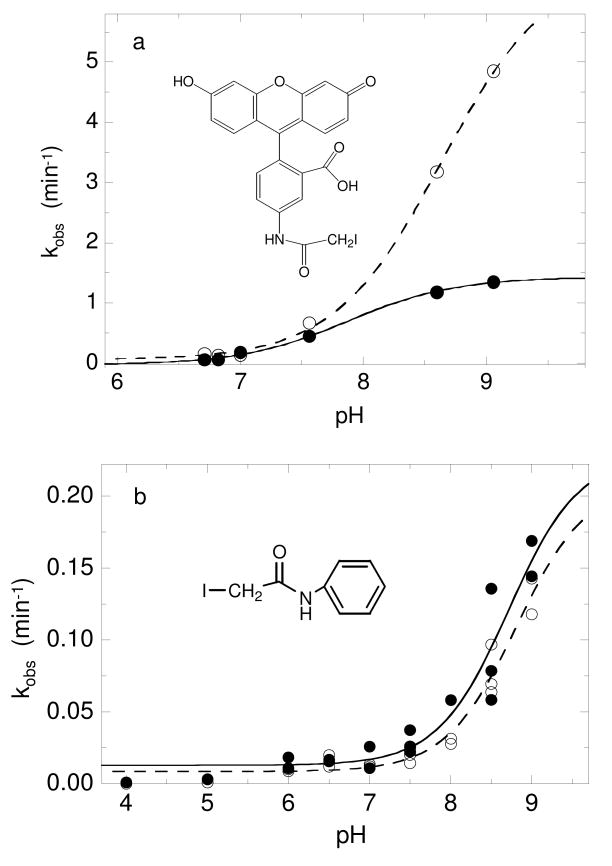
FIGURE 2.
pKa determination using two different iodoacetamide-based compounds and single cysteine mutants of AhpC provide pKa values for C46 and C165 close to 8.5. (a) Reduced C165S (—●—) or C46S (- -○- -) AhpC (24 μM) in various pH buffers was incubated with 180 μM 5-iodoacetamidofluorescein for various amounts of time, quenched with excess 2-mercaptoethanol, then analyzed on a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel to determine the % fluorescence in the protein fraction; the data were fit to a single exponential equation to determine kobs at each pH. Data plotted as kobs versus pH were fit to equation 1 as described in Methods. (b) Reduced wild-type AhpC (40 μM) in various pH buffers was incubated with 400 μM d0-IAAn over a time course, and aliquots were quenched with excess 2-mercaptoethanol. A standard amount of AhpC labeled with d5-IAAn was added to each sample, and the protein was digested with trypsin overnight as described in Experimental Procedures. The extent of alkylation of C46 (—●—) and C165 (- -○- -) was determined by measuring the ratio of the peak intensities at 3836/3841 or 1745/1750 Da, respectively. The ratios were fit to a single exponential equation to determine the kobs and used to calculate the pKa of each residue as in panel (a).