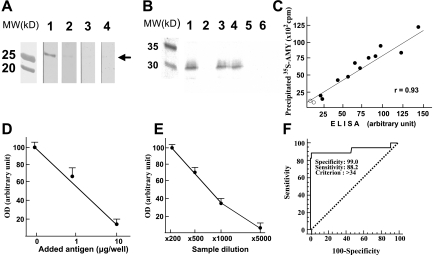
FIG. 2.
Western blot analysis and ELISA for detecting anti-human AMY-2A. A: Western blot analysis. Recombinant human AMY-2A (50 ng) from codons 299 to 512 (AMY-2A/299–512) was electrophoresed in 0.1% SDS–15% polyacrylamide and transferred onto a nitrocellulose filter. The filters reacted with serum (×1,000) from an AIP patient (line 1) and normal control sera (lines 3 and 4). Line 2, AIP patient's serum preincubated with 1 μg/ml AMY-2A/299–512. MW, molecular weight markers. B: Immunoprecipitation of 35S–AMY-2A with antibodies. 35S–AMY-2A was incubated with goat anti-amylase (line 1), normal goat IgG (line 2), sera from AIP patients (lines 3 and 4), and sera from healthy volunteers (lines 5 and 6) and then precipitated with protein G–sepharose. The pellets were electrophoresed in 0.1% SDS–15% polyacrylamide and analyzed with Bas 2000 image analyzer (Fujix, Tokyo). C: Correlation between the result of ELISA and that of immunoprecipitation. By coating the recombinant human AMY-2A/299–512, we developed an ELISA system for detecting anti-human AMY-2A. Sera from 11 patients with AIP (•) and two normal control subjects (○) were assayed by ELISA and immunoprecipitation for detecting the autoantibody. D: Absorption of positive ELISA signal with recombinant AMY-2A. One milliliter of a patient's serum (1:500) was preincubated with the recombinant protein at the indicated dose overnight at 4°C, and then the serum was used as the first antibody. The data are the mean of triplicate values. OD, optical density. E: Serum dilution experiment in ELISA assay. Positive serum from patient A.O. was diluted as indicated, and ELISA assay was carried out. The data are the mean of triplicate values. F: ROC analysis of the healthy volunteers and fulminant type 1 diabetic patients. We carried out ROC analysis of the healthy volunteers (n = 100) and fulminant type 1 diabetic patients (n = 17) with MedCalc.