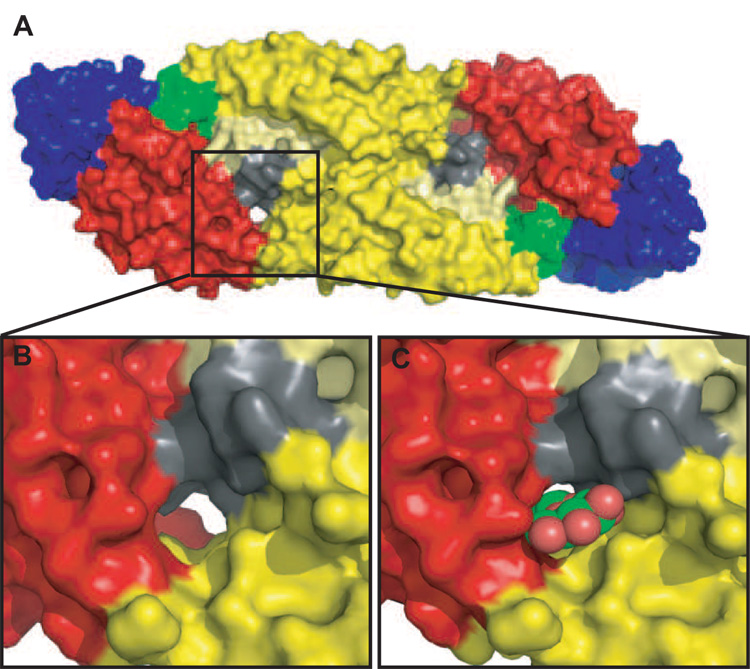
Figure 4. β-OG binding pocket in the E protein.
A. A space-filled representation of the atomic structure of the E protein homodimer (Modis et al., 2003; Y. Zhang et al., 2003). The E proteins are colored as in Figure 2, with the exception of the kl loop (residues 268–280 in DENV-2) (shaded in grey) that is suggested to control the ‘open’ and ‘closed’ confirmation of the β-OG pocket (boxed). This kl loop interacts with the ij loop in DII (residues 237–253 of DENV-2 and shaded in pale yellow) during these conformational changes. B. An enlarged view of the β-OG pocket pocket in its ‘apo’ conformation. Note that the pocket forms a channel with open access at both ends. C. An enlarged view of the pocket with β-OG occupying the pocket.