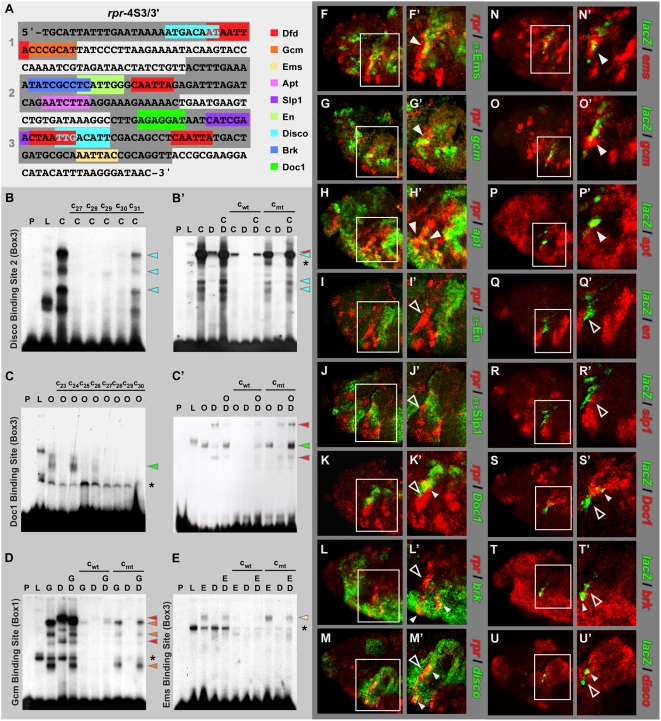
Figure 5. Co-regulatory transcription factors directly interact with rpr-4S3/3′ enhancer.
(A) Sequence of rpr-4S3/3′ enhancer fragment with binding sites for Dfd (shown in red) and all identified co-regulatory transcription factors (highlighted in different colours) is shown. Conserved regions 1 to 3 within the rpr-4S3/3′ enhancer are highlighted as dark grey boxes. (B and C) EMSAs for mapping of Disco binding site 2 (B) and Doc1 binding site (C) using box 3 as shift probe. EMSA was performed using no protein (P), translation lysate only (L), lysate with Dfd protein (D), lysate with Disco protein (C) and lysate with Doc1 protein (O). c27 to c31 in (B) and c23 to c30 in (C) represent consecutive competitor oligonucleotides with their middle base-pairs mutated. Competition experiments revealed that sequences mutated in the oligonucleotide c31 include binding site for the Disco protein (B), whereas oligonucleotides c24 include binding site for the Doc1 protein (C). The turquoise and green arrowheads indicate specific DNA-protein complexes containing either Disco or Doc1 protein, respectively. (B′, C′, D, E) EMSAs using no protein (P), translation lysate (L), lysate with Dfd protein (D), Doc1 protein (O), Gcm protein (G), Ems protein (E) and lysate with Dfd protein (D). To test specificity of binding of the proteins to the DNA fragments, competitor oligonucleotides for the mapped binding sites were used either in their wild-type (cwt) or mutant (cmt) sequence versions. Red arrowheads indicate specific DNA-protein complexes containing Dfd protein, turquoise, green, orange or light-yellow arrowheads indicate specific DNA-protein complexes containing Disco, Doc1, Gcm or Ems proteins, respectively. Note that in all competitor oligonucleotides only binding site sequences for co-regulatory transcription factors are mutated, but not for Dfd binding sites. (F to U′) Protein or RNA co-localization of co-regulatory transcription factors and rpr (F to M′) or lacZ RNA (N to U′) in head of stage 11 wild-type (F to M′) or rpr-4S3 reporter line (N to U′) embryos. Boxes mark maxillary segment with rpr or lacZ RNAs present in anterior part. In (F′ to M′ and N′ to U′) close-ups of maxillary segments are shown. Co-localization of rpr or lacZ RNAs and co-regulator RNA is observed in individual cells for Doc1, Brk, Disco (K′ to M′ and S′ to U′; small, closed arrowheads). Closed arrowheads mark cells co-expressing rpr and lacZ RNAs and RNA or protein of activating co-regulators, open arrowheads highlight areas of rpr or lacZ transcription and missing expression of repressing co-regulators in anterior part of maxillary segments. Asterisks in (B′, C, D and E) indicate complexes with lysate protein seen also in the controls.