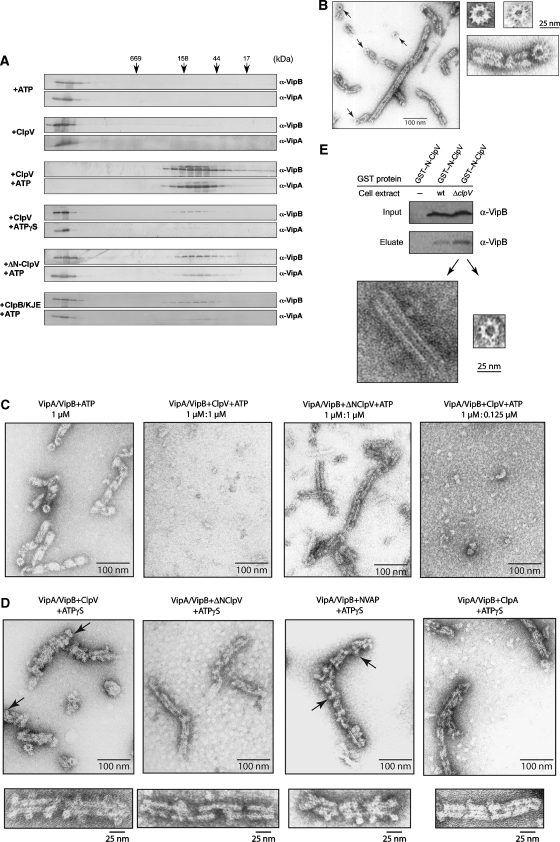
Figure 5.
ClpV converts cogwheel-like VipA/VipB tubules to small complexes. (A) VipA/VipB complexes were incubated in the presence of the indicated components for 30 min at 30°C. Complex integrity was monitored by size-exclusion chromatography and eluted fractions were analysed by immunoblotting using VipA- and VipB-specific antibodies. Elution positions of protein standards are indicated by arrows. (B) Morphology of VipA/VipB complexes monitored by electron microscopy. Arrows indicate cogwheel-like structures. Respective scale bars are given. (C) VipA/VipB complexes were incubated without or with ClpV or ΔN-ClpV (+ATP) for 30 min at 30°C and analysed by electron microscopy. Respective scale bars are given. (D) VipA/VipB complexes were incubated with ClpV, ΔN-ClpV, NVAP1 and ClpA (each+ATPγS) and analysed by electron microscopy. Arrows indicate dot-like structures that are associated with VipA/VipB tubules and exhibiting a central hole. Respective scale bars are given. (E) Purified GST–N-ClpV was coupled to glutathione beads and incubated with soluble cell extracts of V. cholerae V52 wild type and ΔclpV. Bound proteins were eluted by the addition of glutathione and analysed by immunoblot analysis using VipB-specific antibodies and by electron microscopy. Equal amounts of VipB present in the used cell extracts were confirmed by western blot (input control).