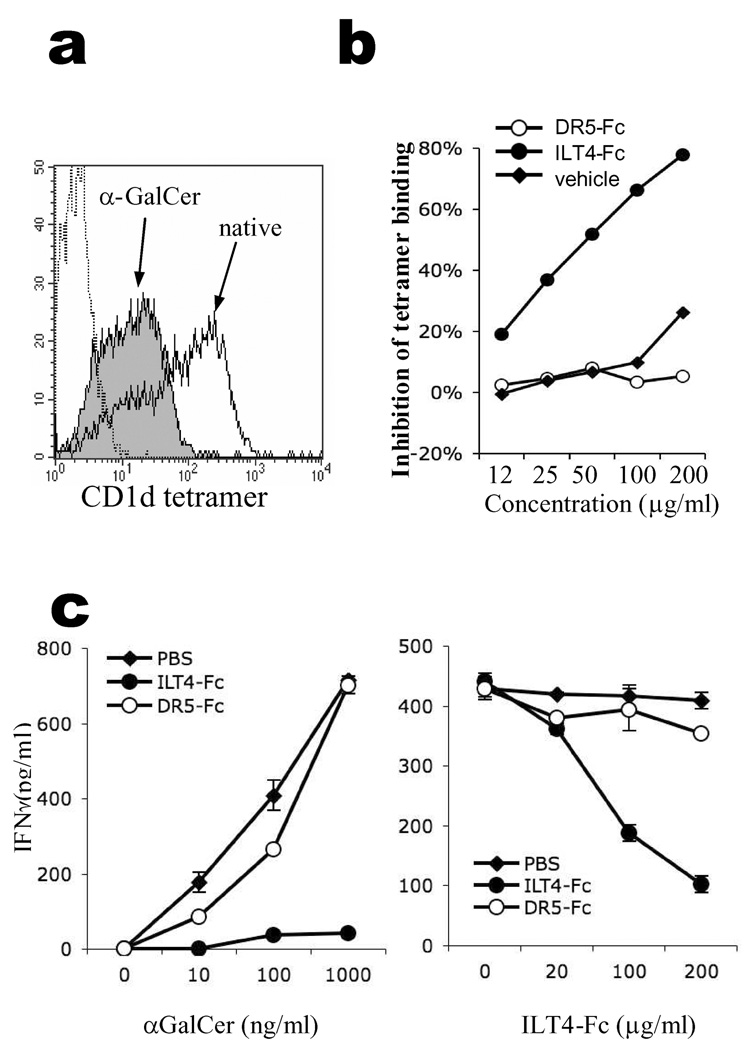
Figure 6.
ILT4 regulates APC-NKT recognition in an antigen-dependent manner. (a) Blocking of CD1d binding to ILT4 by αGalCer. HEK293T-ILT4 cells were stained with native (open histogram) or αGalCer-loaded CD1d tetramers (filled histogram). PE-conjugated Streptavidin was used as negative control staining (dotted line). (b) Blocking of αGalCer loading to CD1d by ILT4. Native CD1d-tetramers were pre-incubated with different concentrations of ILT4-Fc (filled circles), or control protein DR5-Fc (open circles) before being pulsed with αGalCer antigen. The resultant αGalCer-CD1d tetramers were used to stain NKT cells and MFI of the stainings were compared to calculate the inhibition rates. As a control, pre-generated αGalCer-CD1d tetramers were used to stain NKT cells in the presence of various concentrations of ILT4-Fc protein (filled diamonds). Results from one out of three repeated experiments are shown. (c) IFNγ secretion by a NKT cell line (NKN) stimulated by plate-bound CD1d protein. Plate-bound CD1d were incubated with 200µg/ml of ILT4-Fc, control protein DR5-Fc or solvent PBS, before being pulsed with different concentrations of αGalCer (left panel). In the right panel, the plates were incubated with different concentrations of blocking reagents before being pulsed with 100ng/ml of αGalCer.