Abstract
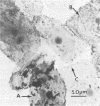
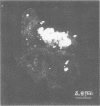
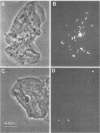
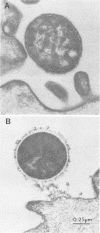
The relationship between the variability in the fibronectin (Fn) content on human buccal epithelial cells and the capacity of the cells to bind gram-positive (Streptococcus pyogenes) or gram-negative (Escherichia coli or Pseudomonas aeruginosa) bacteria was investigated. Adhesion experiments performed with mixtures of epithelial cells and mixed suspensions of either S. pyogenes and E. coli or S. pyogenes and P. aeruginosa exhibited three major populations of buccal cells: one of these was able to bind S. pyogenes (gram positive) but neither of the gram-negative bacteria; a second population was able to bind the gram-negative but not the gram-positive bacteria; and a third was able to bind various numbers of both types of organisms. Further adhesion experiments performed with a mixture of epithelial cells and a mixed suspension of S. pyrogens, E. coli, and fluoresceinconjugated methacrylate beads coated with immune immunoglobulin G directed against Fn revealed that the epithelial cells recognizing the gram-positive bacteria were rich in Fn, whereas those recognizing the gram-negative organisms were poor in Fn. Immunoelectron microscopy confirmed that cells of S. pyogenes bound to epithelial cells coated with Fn, whereas cells of E. coli bound to epithelial cells lacking Fn. These results suggest that Fn on the surfaces of epithelial cells may modulate the ecology of the human oropharyngeal cavity, especially with respect to the colonization of these surfaces by pathogenic gram-negative or gram-positive bacteria.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babu J. P., Simpson W. A., Courtney H. S., Beachey E. H. Interaction of human plasma fibronectin with cariogenic and non-cariogenic oral streptococci. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):162–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.162-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. B., Murray A., Segal R. A., Bushnell A., Walsh M. L. Studies on intercellular LETS glycoprotein matrices. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):377–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90123-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch E., Balian G., Holbrook K., Duksin D., Bornstein P. Amniotic fluid fibronectin. Characterization and synthesis by cells in culture. J Cell Biol. 1978 Sep;78(3):701–715. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.3.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguid J. P., Clegg S., Wilson M. I. The fimbrial and non-fimbrial haemagglutinins of Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol. 1979 May;12(2):213–227. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-2-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Boesman-Finkelstein M., Holt P. Vibrio cholerae hemagglutinin/lectin/protease hydrolyzes fibronectin and ovomucin: F.M. Burnet revisited. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1092–1095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedman K., Vaheri A., Wartiovaara J. External fibronectin of cultured human fibroblasts is predominantly a matrix protein. J Cell Biol. 1978 Mar;76(3):748–760. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.3.748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P., Vaheri A., Palo J., Ruoslahti E. Demonstration of fibronectin in human cerebrospinal fluid. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Oct;92(4):595–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Amrani D. L. The structure and biologic activities of plasma fibronectin. Blood. 1980 Aug;56(2):145–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F. Fibronectin. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1980;5:111–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B., Kuusela P. Binding of human fibronectin to group A, C, and G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):29–34. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.29-34.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A., Mosher D. F., Olbrantz P. J. Fibronectin binding to Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14788–14794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Engvall E., Hayman E. G. Fibronectin: current concepts of its structure and functions. Coll Relat Res. 1981;1(1):95–128. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(80)80011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydén C., Rubin K., Speziale P., Hök M., Lindberg M., Wadström T. Fibronectin receptors from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3396–3401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Adherence of group A streptococci to fibronectin on oral epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):275–279. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.275-279.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Hasty D. L., Mason J. M., Beachey E. H. Fibronectin-mediated binding of group A streptococci to human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):805–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.805-810.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switalski L. M., Ljungh A., Rydén C., Rubin K., Hök M., Wadström T. Binding of fibronectin to the surface of group A, C, and G streptococci isolated from human infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;1(6):381–387. doi: 10.1007/BF02019939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Water L., Destree A. T., Hynes R. O. Fibronectin binds to some bacteria but does not promote their uptake by phagocytic cells. Science. 1983 Apr 8;220(4593):201–204. doi: 10.1126/science.6338594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Bass J. A., Johanson W. G., Jr, Straus D. C. Role of adherence in the pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):694–699. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.694-699.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Straus D. C., Johanson W. G., Jr, Bass J. A. Role of fibronectin in the prevention of adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to buccal cells. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jun;143(6):784–790. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.6.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Straus D. C., Johanson W. G., Jr, Bass J. A. Role of salivary protease activity in adherence of gram-negative bacilli to mammalian buccal epithelial cells in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1435–1440. doi: 10.1172/JCI110395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetter B. R., Daniels T. E., Quadra-White C., Greenspan J. S. LETS protein in normal and pathological human oral epithelium. J Dent Res. 1979 Jan;58(1):484–488. doi: 10.1177/00220345790580010401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]