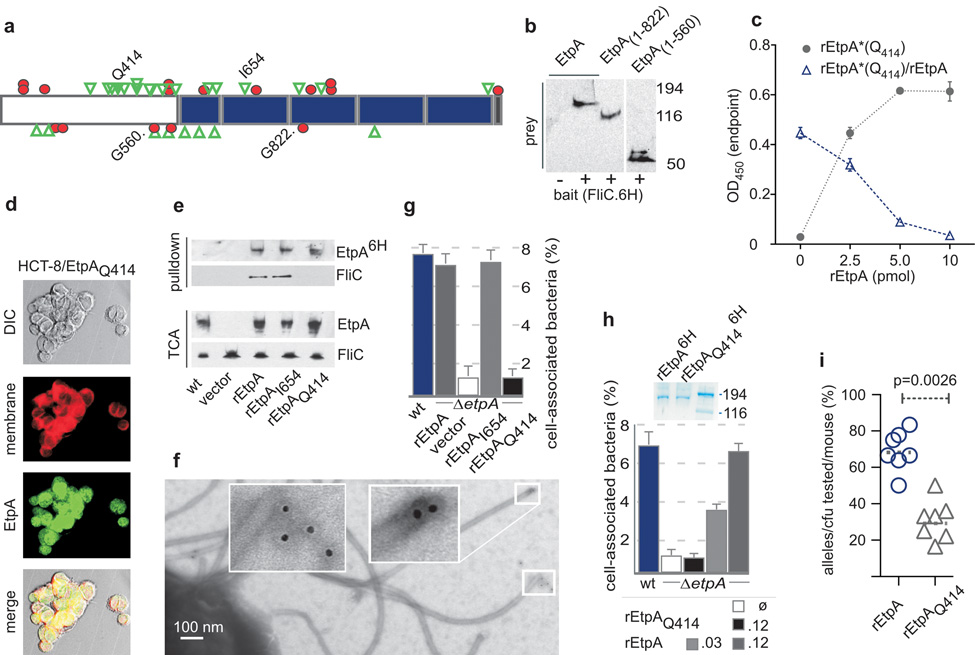
Figure 4. ETEC adherence to epithelial cells in vitro and small intestinal colonization require the interaction of EtpA and flagellin.
a, Linker scanning mutation map of EtpA (blue=repeats, red circles = stop codons, green triangles = in-frame insertions). b, Truncated N-terminal region of EtpA (M1-G560) is sufficient to interact with flagellin (H48) polyhistidine-tagged (FliC.6H) bait in molecular pull-downs. c, EtpAQ414 retains specific binding to Caco-2 cells. Circles=biotinylated (rEtpA*Q414). Triangles=competition with unlabelled rEtpA [mean (n=3) values ± s.e.m.]. d, EtpAQ414 retains binding to HCT-8 epithelial cells surfaces (confocal microscopy). e. EtpAQ414 does not interact with flagellin. etpA mutant (jf1668) was complemented with myc-polyhistidine-tagged EtpA variants as indicated prior to pull-down studies of supernatants with metal affinity resin. f, rEtpA-myc-6H identified with anti-myc 1° monoclonal antibody at flagellar tips of etpA mutant (jf1668) expressing pJY017. g, EtpAQ414 expression in isogenic etpA mutant (jf1668) fails to complement adherence (Caco-2) defect. h, Exogenous rEtpA, but not rEtpAQ414 complements the adherence defect in the etpA mutant. SDS-PAGE above the graph shows rEtpA(6H) and rEtpAQ414(6H) used in assays. (key = final [nM] concentrations). i, EtpAQ414 fails to complement colonization defect when expressed in isogenic etpA mutant. Graph shows the proportion of cfu bearing either the wild type allele (carried on pJL017) or mutant allele (carried on pJMF1087) recovered from each mouse (N=7) following simultaneous challenge with 1 × 104cfu of both strains. p=0.0026 (two-tailed Mann-Whitney test). An average of 15 colonies per mouse were analyzed by PCR and PmeI digestion.