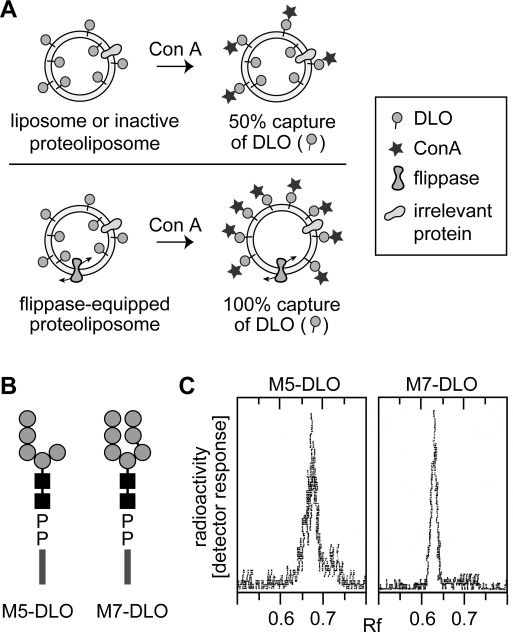
Figure 2.
Strategy for assaying DLO translocation in reconstituted vesicles. (A) Assay for assessing DLO flipping in reconstituted vesicles. Unilamellar vesicles with [3H]DLO symmetrically distributed across the membrane are incubated with Con A. Con A captures DLO species that are initially located in the outer leaflet, as well as those that gain access to the outer leaflet after being translocated from the inner leaflet through the action of a flippase. After Con A binding is allowed to go to completion, the sample is extracted with organic solvent. DLOs that are bound to Con A precipitate with the protein, while free DLOs are extracted. In liposomes or inactive proteoliposomes (vesicles containing membrane proteins but not a flippase), 50% of the [3H]DLOs are expected to be captured by Con A, corresponding to the pool of DLO in the outer leaflet. [3H]DLOs in the inner leaflet of these vesicles cannot access Con A and are extracted by the solvent (top panel). For proteoliposomes containing a flippase (bottom panel), Con A binds all [3H]DLOs since those originally in the inner leaflet are flipped to the outer leaflet and captured by the lectin; thus, ∼100% of the DLOs are expected to be precipitated with Con A in this situation. In mixtures of vesicles in which some possess a flippase while others do not, the percent of [3H]DLO captured by Con A is predicted to be intermediate between 50 and 100%, reflecting the proportion of flippase-containing vesicles in the population. (B) Structures of M5-DLO and M7-DLO. The symbols used for dolichol, mannose, and GlcNAc are as described in the legend of Figure 1. The chemical structure of the oligosaccharide moiety of M5-DLO is Manα1−2Manα1−2Manα1−3(Manα1−6)Manβ1−4GlcNAcβ1−4GlcNAc; the oligosaccharide moiety of M7-DLO is Manα1−2Manα1−2Manα1−3(Manα1−2Manα1−3Manα1−6)Manβ1−4GlcNAcβ1−4GlcNAc. (C) Thin layer chromatography of [3H]M5-DLO and [3H]M7-DLO. Radiolabeled M5-DLO and M7-DLO were prepared from [3H]mannose-labeled yeast as described in . An aliquot of each preparation was analyzed by thin layer chromatography; chromatograms were visualized using a Berthold LB2842 radioactivity scanner. Each chromatogram contained a single peak of radioactivity; the relevant section of the chromatograms is shown.