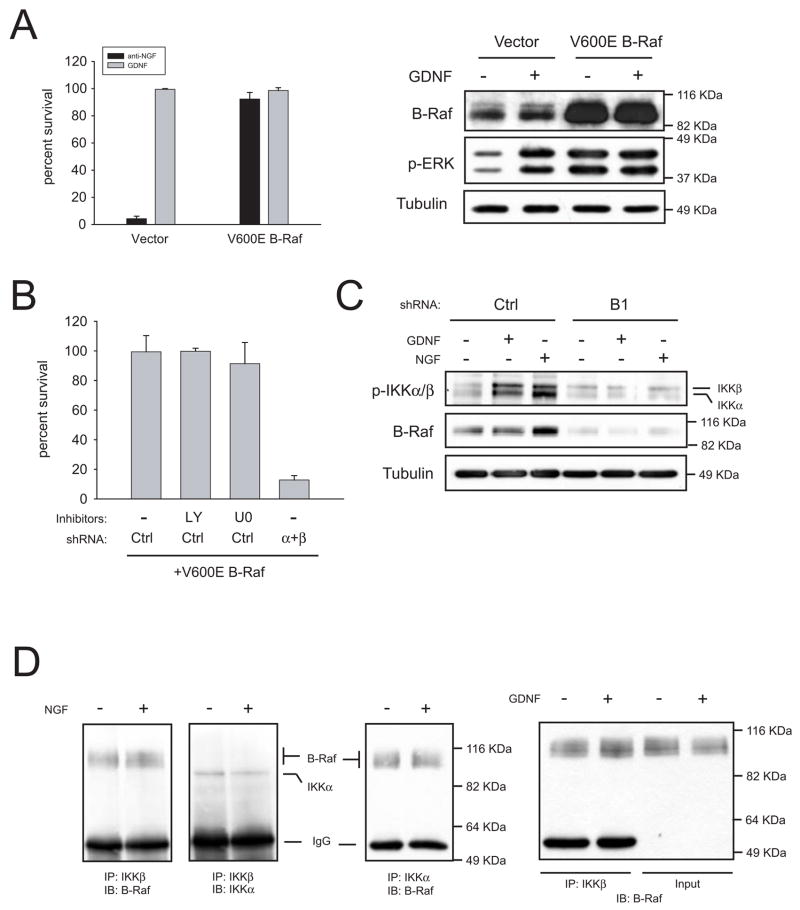
Figure 7.
IKKα and IKKβ are downstream effectors of B-Raf. (A) A constitutively active form of B-Raf (V600E) rescues trophic factor-deprived neurons. Left, cells were infected with a lentiviral construct coding for human V600E B-Raf or empty vector. Four days later, cells were switched to media containing a blocking anti-NGF antibody or GDNF. Survival was assessed after 48h in the presence of GDNF. Right, V600E B-Raf mutant is constitutively active. Cells infected with V600E B-Raf or empty vector were stimulated with for 10 minutes with GDNF and lysates probed with antibodies to B-Raf and dually phosphorylated ERK1/2. (B) Silencing of IKKs, but not inhibition of PI 3-K or MEK, reverses the protection afforded by V600E B-Raf. Cells were sequentially infected as described in methods with V600E B-Raf, and either control shRNAs or a mixture of shRNAs to IKKα and IKKβ (“α+β”). Three days after cells were deprived and kept in the presence of the indicated inhibitors (10 μM each) two additional days, after which survival was evaluated. (C) B-Raf acts upstream of IKKs. Cells were infected with control shRNAs or a shRNA to B-Raf (“B1”). Four days after infection, cells were deprived overnight in the presence of 50 μM BAF. Cells were stimulated for 10 minutes with the indicated factors and lysates probed against phospho-IKKs, B-Raf or tubulin. (D) Endogenous IKKs and B-Raf form a complex in sympathetic neurons. Neurons were kept in NGF for five days, deprived overnight and stimulated for 10 minutes with medium alone or containing the indicated factor. IKKβ or IKKα were immunoprecipitated and lysates were immunoblotted (IB) with the indicated antibodies. In the right panel, 5% of the input lysate was resolved in parallel to IKKβ immunoprecipitates.