Figure 6. NLS1 of the Eag C-terminal is required for morphological effects in COS cells.
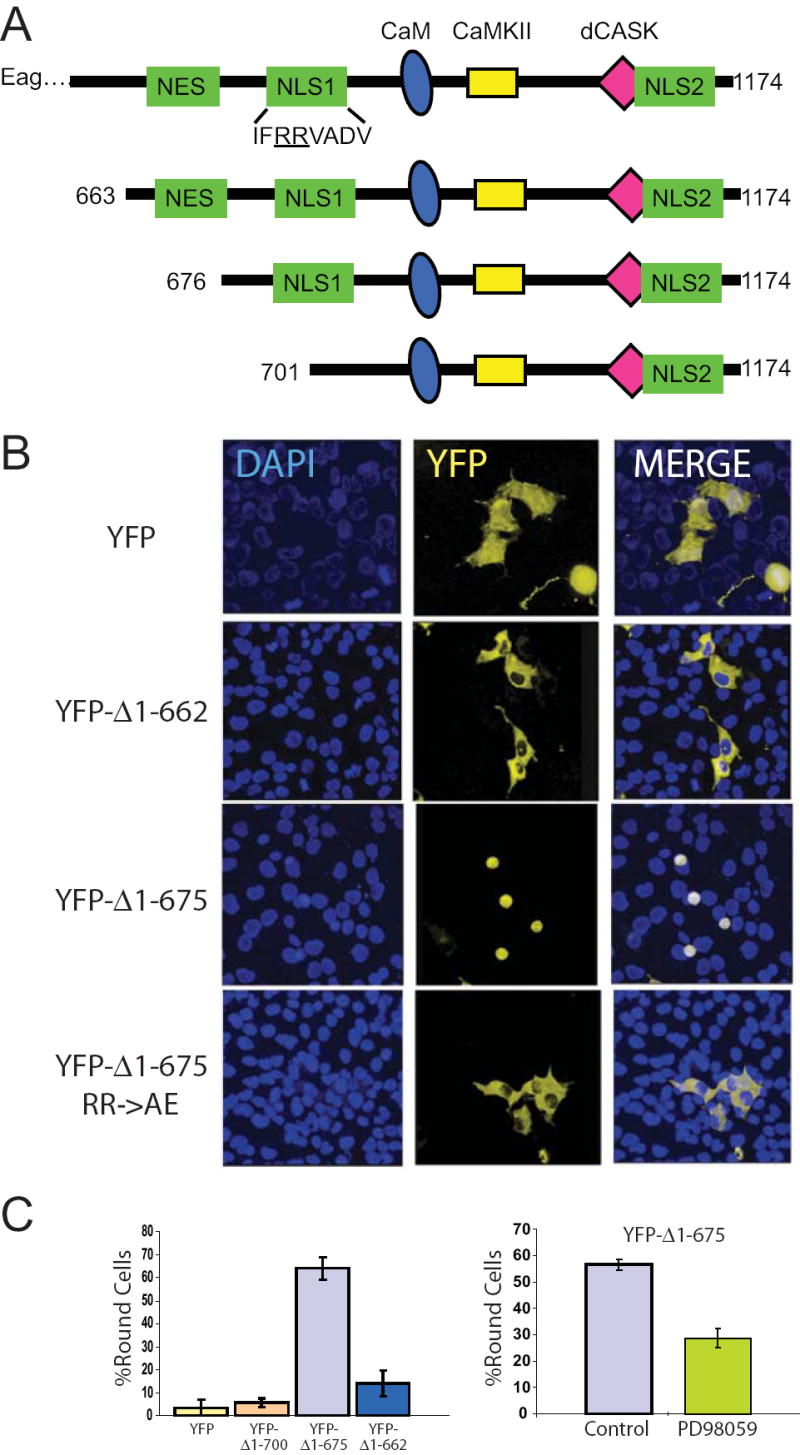
(A) Cartoon of Eag C-terminal domains and constructs. The Eag protein has multiple signaling modules including putative nuclear export (NES) and nuclear localization (NLS) sequences. It also contains binding sites for calmodulin (CaM), calcium/CaM-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) and dCASK. (B) Three YFP-tagged Eag C-terminal fragments (YFP-Δ1-662, which contains the putative NES, YFP-Δ1-675, which lacks the NES but contains both NLSs, and YFP-Δ1-662 with a point mutation in NLS1) were expressed in COS cell for 29 hours. Two examples of YFP-Δ1-675 are shown at different stages of the rounding process. YFP alone was expressed as control. DAPI staining shows nuclei. Scale bar = 30 μm. (C) Left panel, percentage round cells is shown for YFP, YFP-Δ1-700, which lacks both the NES and NLS1, YFP-Δ1-675 and YFP-Δ1-662. Right panel, MAPK inhibitor PD98059 (50 μM), added 6 h after transfection, inhibits YFP-Δ1-675-dependent cell rounding.
