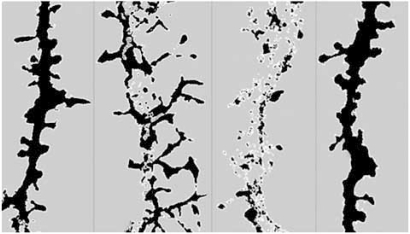
Fig. (2).
ADDL binding to dendritic spines causes time-dependent changes in dendritic spine morphology and density as illustrated here by drebrin immunoreactivity, a dendritic spine marker. Computer-derived profile outlines were generated from a z-stack reconstruction of single dendritic branche imaged from a confocal scanning of drebrin-immunolabeled neurons. The treatment conditions represented here were in the following order ADDL 500nM for 5min, ADDL 500nM for 6hrs, ADDL 500nM for 24hrs and Vehicle for 24hrs. The same threshold setting was applied under the treatment conditions and show that both the dendritic spine density was decreased after ADDL treatment and that some spines are abnormally long after a prolonged ADDL treatment.