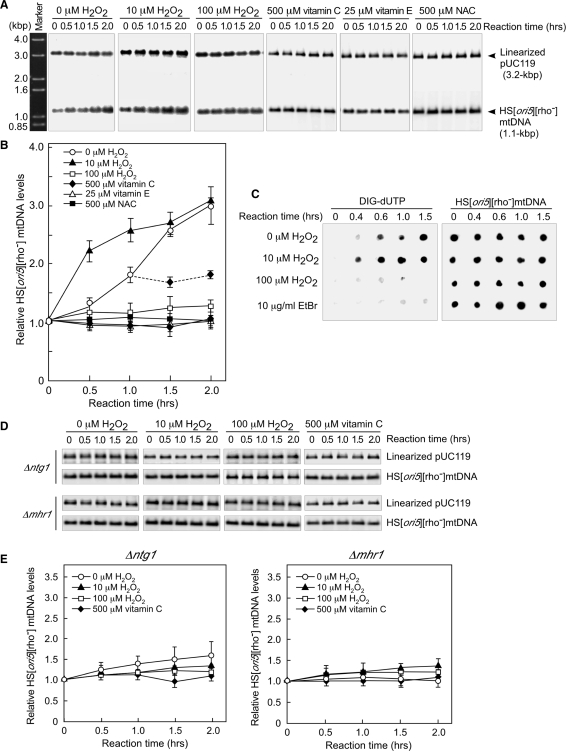
Figure 2.
Changes in mtDNA copy number in isolated mitochondria treated with 10 μM hydrogen peroxide. (A) Treatment with 10 μM hydrogen peroxide increased mtDNA copy number in mitochondria isolated from wild-type cells. Isolated mitochondria were incubated with the indicated concentrations of hydrogen peroxide. mtDNA was digested with BglII and separated by electrophoresis on a 1.0% agarose gel. Marker, 1.0-kbp plus ladder. (B) Quantitative analysis of the relative mtDNA copy number in mitochondria isolated from wild-type cells. Vitamin C (500 μM), 25 μM vitamin E or 500 μM NAC were added to the incubation buffer from the start time point. After 1 h of incubation, mitochondria not treated with hydrogen peroxide were transferred into fresh incubation buffer containing 500 μM vitamin C. The average values from three independent experiments are plotted in (B). (C) Newly synthesized mtDNA (left panel) and total mtDNA (right panel) in isolated mitochondria. Mitochondria isolated from wild-type cells were incubated with DIG-dUTP, which was detected using anti-DIG AP conjugates. Total mtDNA was detected by Southern dot-blotting analysis using 32P-labeled 1.1-kbp HS [ori5] [rho–] mtDNA as the probe. (D) A low concentration (10 μM) of hydrogen peroxide did not induce an increase in mtDNA copy number in mitochondria isolated from either ntg1-null or mhr1-null cells. There was no change in mtDNA copy number when mitochondria isolated from either ntg1-null or mhr1-null cells were incubated with vitamin C. (E) Quantitative analysis of mtDNA copy number in mitochondria isolated from either ntg1-null or mhr1-null mutant cells. The average values from three independent experiments are plotted.