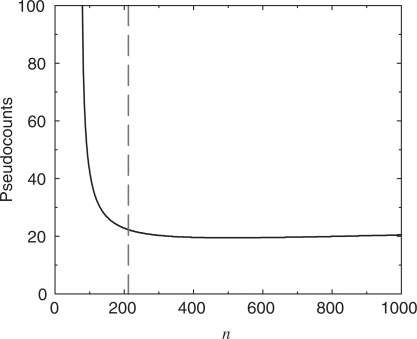
Figure 6.
Optimal number of pseudocounts, m, as a function of the number of independent observations, n. Using the data listed in Table 3 and the method illustrated in Figure 5, we found the optimal number of pseudocounts for varying n. The method cannot be valid for n < 212 (vertical dotted line), because the calculated decrease in model description length for 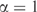 is greater than the description length of the model at
is greater than the description length of the model at  , but it is not possible for a model to have a negative description length. For n between 212 and 1000, the calculation suggests we use a nearly constant number m of pseudocounts, roughly 19.4. In the limit of very large n, the MDL principle suggests the number of pseudocounts should grow proportionately to n1/3.
, but it is not possible for a model to have a negative description length. For n between 212 and 1000, the calculation suggests we use a nearly constant number m of pseudocounts, roughly 19.4. In the limit of very large n, the MDL principle suggests the number of pseudocounts should grow proportionately to n1/3.