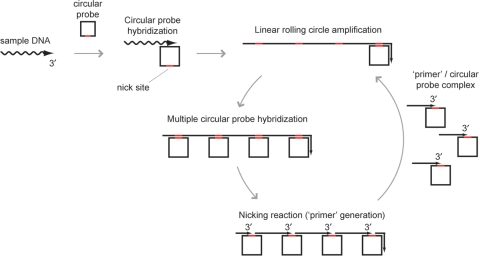
Figure 1.
Reaction mechanism of PG–RCA. PG–RCA initiates from hybridization between a sample DNA and a circular probe (Step 1). Once a sample DNA and circular probe form a complex, DNA polymerase synthesizes a long concatenated sequence copy of the circular probe through linear rolling circle amplification (LRCA) (Step 2). Then, multiple circular probes hybridize to multiple sites of the LRCA product, and nicking enzyme recognition sequences of the LRCA product are activated by double strand formation (Step 3). Nicking enzyme recognizes and cleaves the recognition sequences and produces multiple complexes of a ‘primer’ and circular probe (Step 4). Each complex can initiate the next round of PG–RCA (go back to Step 2).