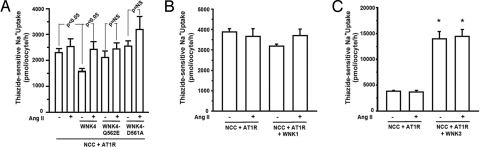
Fig. 2.
Effects of AngII signaling in the presence of PHAII-WNK4, WNK1 and WNK3. (A) PHAII mutant WNK4 phenocopys the effect of AngII. Thiazide-sensitive 22Na+ uptake was measured in oocytes injected with NCC and AT1R alone or together with wild-type WNK4 or WNK4 harboring either the Q562E or D561A PHAII mutation in the presence or absence of AngII. Unlike WT-WNK4, PHAII-WNK4s show no significant inhibition of NCC activity, and AngII signaling imparts no significant further increase in NCC activity. (B and C) AngII signaling does not alter NCC activity in the presence of WNK1 or WNK3. Thiazide-sensitive 22Na+ uptake was measured as in panel A except that WNK1 or WNK3 has been substituted for WNK4. WNK1 has no effect on NCC in the presence or absence of AngII; WNK3 markedly increases NCC activity as previously described, however, AngII signaling does not modulate this effect. *, significantly different from the uptake observed in NCC+AT1R group in the absence of AngII.