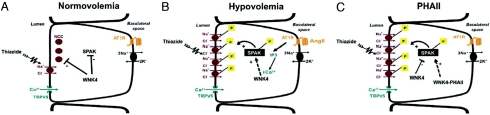
Fig. 6.
Proposed model for AngII modulation of WNK4-SPAK-NCC interaction in physiological conditions and pathophysiological conditions. Epithelial cells of the DCT are shown. (A) In normovolemia, AngII levels are low, and WNK4 inhibits activation of NCC via inhibition of phosphorylation of SPAK and NCC. (B) In hypovolemia, AngII levels and AT1R signaling are increased, WNK4 inhibition of SPAK/NCC is prevented, and NCC activity increases via increased trafficking of the phosphorylated cotransporter to the plasma membrane. (C) PHAII-WNK4 alleviates WNK4 inhibition of SPAK, leading to SPAK phosphorylation and increased delivery of NCC to the plasma membrane.