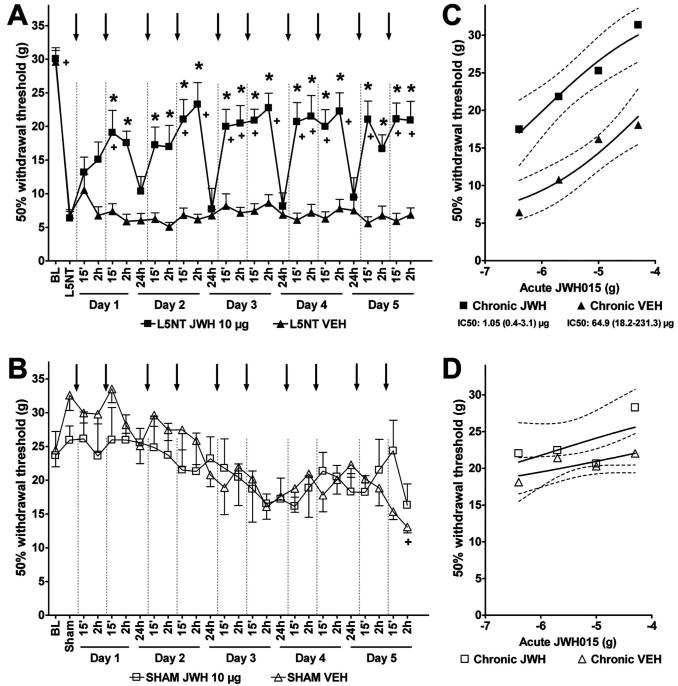
Fig. 9.
Effects of chronic intrathecal administration of JWH015 and tolerance study. Withdrawal thresholds to von Frey stimulation ipsilateral to L5 nerve transection (L5NT) (A) or sham (B) surgery before (baseline [BL]) and 4 days after surgery (L5NT or Sham), and 15 min and 2 h after the first intrathecal injection and 15 min, 2 h, and 24 h after the second intrathecal injection (arrows and dotted lines) of vehicle (VEH, n = 7 for L5NT and n = 3 for sham) or 10 μg JWH015 (JWH 10 μg, n = 8 for L5NT and n = 5 for sham) during 5 consecutive days. Over time, values versus after-surgery data (L5NT or Sham) significantly differ by Friedman test; + P < 0.05 versus L5NT in A or Sham in B by Friedman test followed by Wilcoxon test. Groups significantly differ by Kruskal-Wallis test in A but not in B;* P < 0.05 compared with vehicle group by Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Mann-Whitney U test. (C and D) Withdrawal thresholds (95% confidence limits, dotted lines) to von Frey stimulation ipsilateral to L5NT (C) or sham (D) surgery 15 min after escalating doses (0.4, 2, 10, and 50 μg) of intrathecal JWH015 administered 24 h after the chronic treatment with 10 μg JWH015 (chronic JWH) or vehicle (chronic VEH). Groups significantly differ by Kruskal-Wallis test in C but not in D; all doses were significantly different between both groups in C (P < 0.05) by Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Mann-Whitney U test. IC50s were significantly different by t test in C (P < 0.05).