Figure 5.
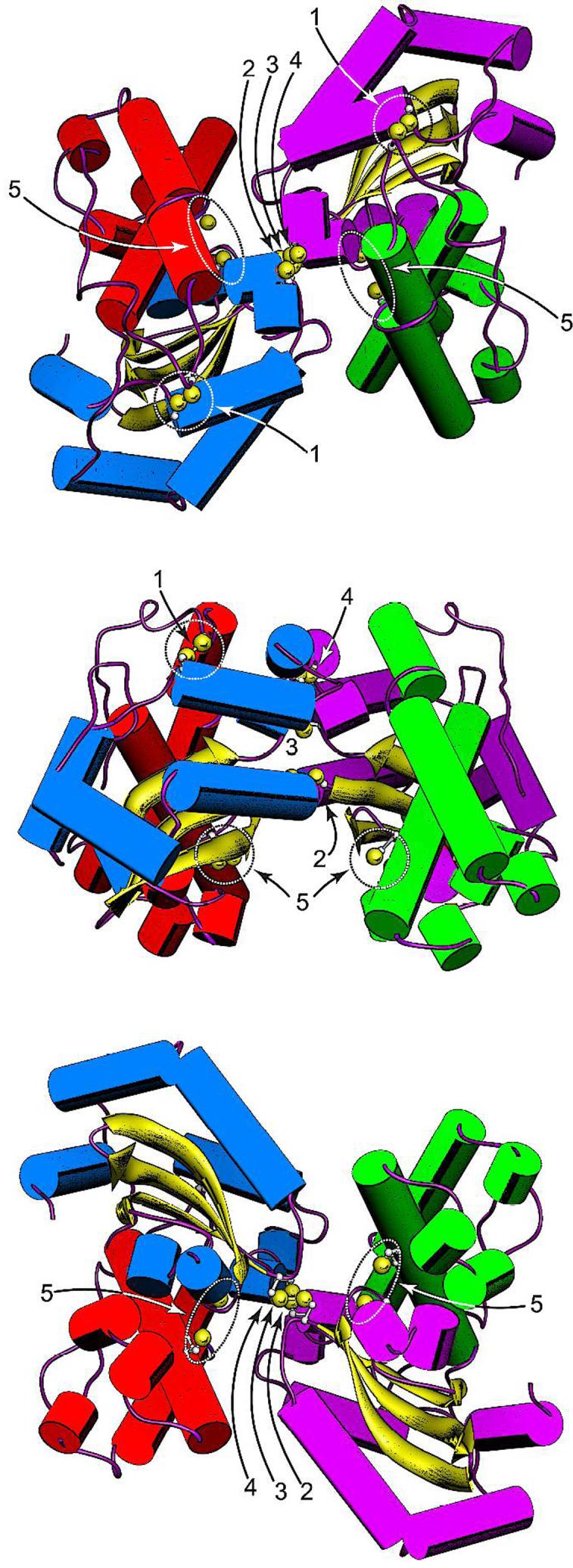
Disulfide constraints introduced into the EC MnSOD structure by Cys substitution mutagenesis. (Top) Top view of the MnSOD dimer, parallel to the molecular two-fold axis on the N-terminal domain side. (Middle) Side view of the MnSOD dimer, perpendicular to the molecular twofold axis. (Bottom) Bottom view of the MnSOD dimer, parallel to the molecular two-fold axis on the C-terminal domain side. The cysteines shown are hypothetical structures based on replacement of the corresponding residues in WT MnSOD (PDB ID 1vew) with Cys and manually adjusting the side chain dihedrals. Cysteines are rendered with ball-and-stick side chains, with Cys SG sulfur shown as a van der Waals sphere. In each view, the individual domains and subunits are identified by helix color. Subunit A: N-domain, green; C-domain, purple. Subunit B: N-domain, red; C-domain, blue. (1) H17CN190C disulfide; (2) S126CA-S126CB disulfide; (3) E170CA-E1706CB disulfide; (4) Y174CA-Y174CB disulfide; (5) R72C, D147C pair. Rendered using Chimera (Ref. 13).
