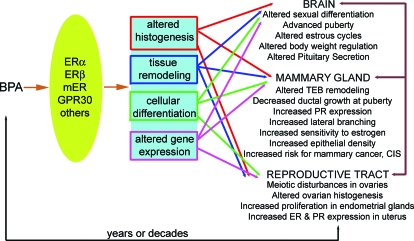
Figure 4.
Proposed mechanisms for the endpoints affected in perinatally BPA-exposed females. BPA binds ERs, including the classical ERs (ERα and ERβ) and mERs. This causes alterations at several levels of organization including tissues, cells, and gene expression. These alterations lead to diverse changes in estrogen-target organs including the brain, mammary gland, ovary, and uterus, among others. Additionally, changes in one target organ can lead to secondary alterations in other organs. In addition to these classical targets, other nonclassical targets of BPA action include bone, cardiovascular tissue, the pancreas, adipose tissue, and the immune system (not pictured).