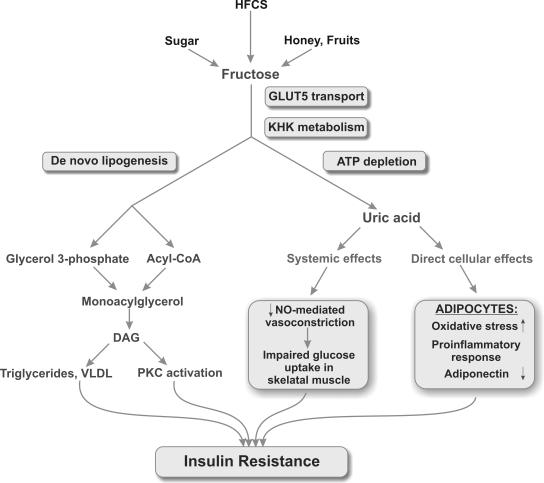
Figure 3.
Potential mechanisms by which fructose and uric acid may induce insulin resistance. Fructose enters cell via a transporter (primarily Glut 5) where it is acted on by fructokinase (KHK). As part of this metabolism, ATP depletion may occur, generating uric acid with systemic effects that block insulin-dependent NO-mediated vascular dilation as well as direct cellular effects on the adipocyte. Fructose also causes de novo lipogenesis that can lead to intracellular triglycerides that can also induce insulin resistance. DAG, Diacylglycerol; PKC, protein kinase C; VLDL, very low-density lipoprotein.